Building distributed applications doesn’t have to be a nightmare. Here’s how .NET Aspire transforms your development experience.

What is .NET Aspire?
.NET Aspire is Microsoft’s opinionated stack for building observable, production-ready, cloud-native applications. Think of it as your personal DevOps assistant that handles all the tedious plumbing while you focus on what matters: building great software.
But here’s the kicker – it’s not just another framework. It’s a complete development experience that bridges the gap between local development and production deployment.
The Modern Developer’s Dilemma
Picture this: You’re building a modern web application. It needs a database, a cache, maybe a message queue, and several microservices. Before you know it, you’re juggling Docker containers, managing connection strings, wrestling with service discovery, and spending more time on infrastructure than actual features.
Sound familiar? You’re not alone. This is where .NET Aspire steps in as your knight in shining armor.
The Docker Compose Struggle: Why Traditional Approaches Fall Short
Before we dive deeper into Aspire’s capabilities, let’s talk about the elephant in the room – Docker Compose. Many developers have been using Docker Compose to orchestrate their multi-service applications, and while it works, it comes with significant pain points that Aspire elegantly solves.
Typical Challenges of Relying Solely on Docker Compose
1. Complex Service Discovery Management
When using Docker Compose, services finding and communicating with each other typically rely on:
- Hardcoded hostnames in configuration
- Using container names as DNS
- Manual port mapping management
Here’s what a typical Docker Compose setup looks like for our e-commerce application:
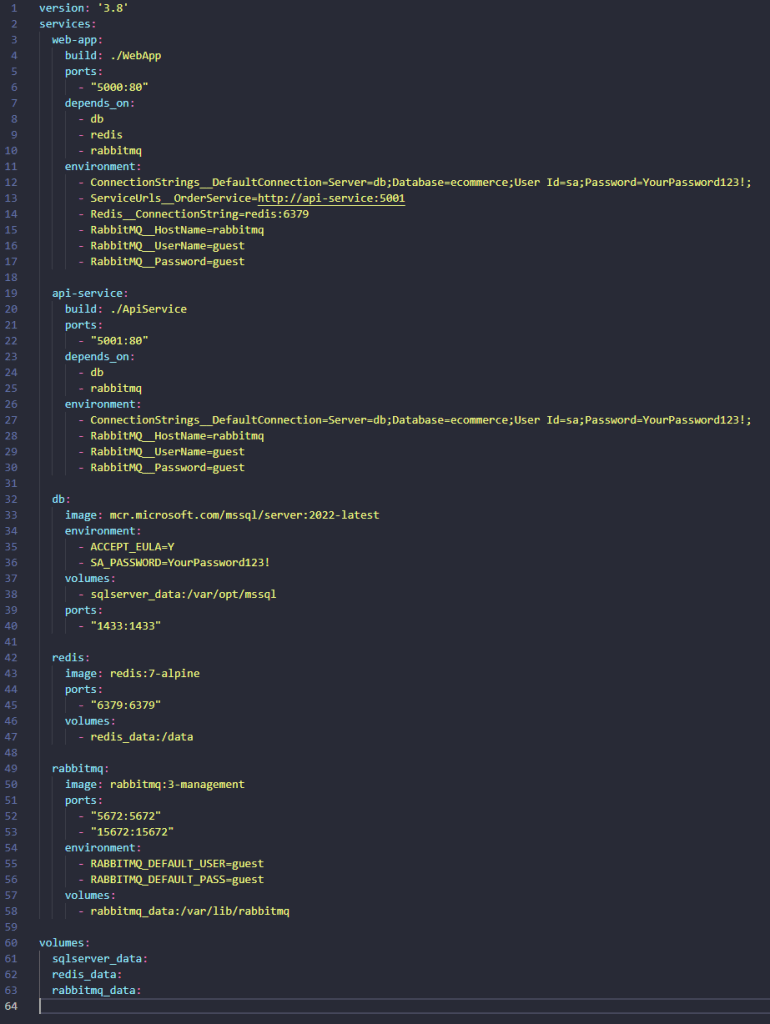
In your .NET code, you must manually configure service URLs
Issue: As the number of services increases, managing these dependencies becomes extremely complex and error-prone.
2. Lack of Integrated Observability Support
Docker Compose doesn’t provide:
- Automatic distributed tracing
- Metrics collection
- Centralized logging
- Health check monitoring
You have to manually set up Prometheus, Grafana, Jaeger, ELK stack:
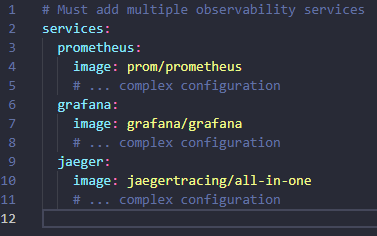
3. Poor Development Experience
- Must restart entire stack when changing one service
- Complex debugging with multiple services
- No unified logging in development
- Difficult to track request flow across services
How .NET Aspire Solves These Problems
Before we dive into how .NET Aspire helps solve real-world challenges, let’s first create a sample Aspire project by following the official guide:
Build your first Aspire app
Once you’ve successfully set up your Aspire project, feel free to check out my GitHub repository for a sample setup that includes RabbitMQ, Redis, and SQL Server:
CloudNativeEcommerce GitHub Repo
For the scope of this post, I’ll focus on integrating SQL Server with the ApiService.
Now let’s see what Aspire can do
1. Automatic and Type-safe Service Discovery
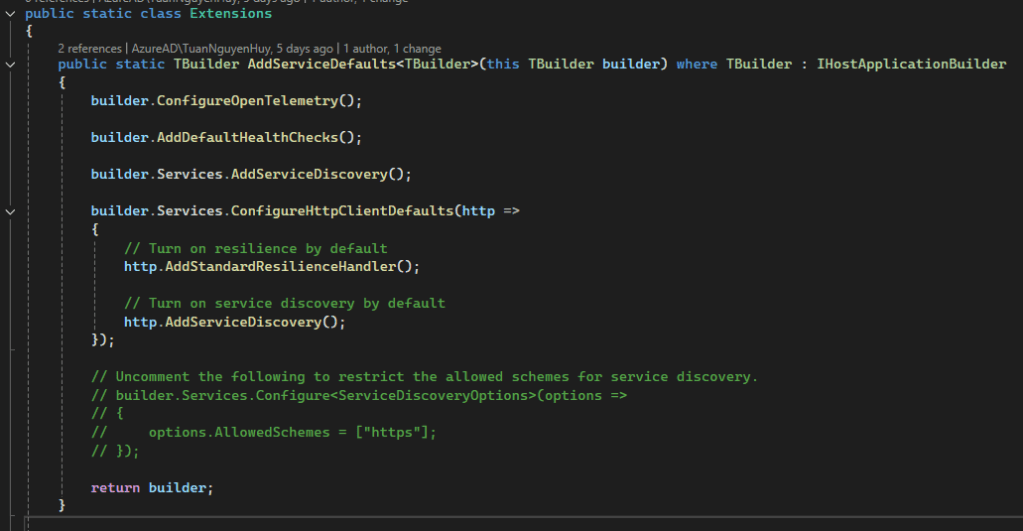
.NET Aspire provides many integrations and automatic service discovery to help you build cloud-native applications. Now you can easy setup them in AppHost instead Docker compose (.NET Aspire integrations overview – .NET Aspire | Microsoft Learn)
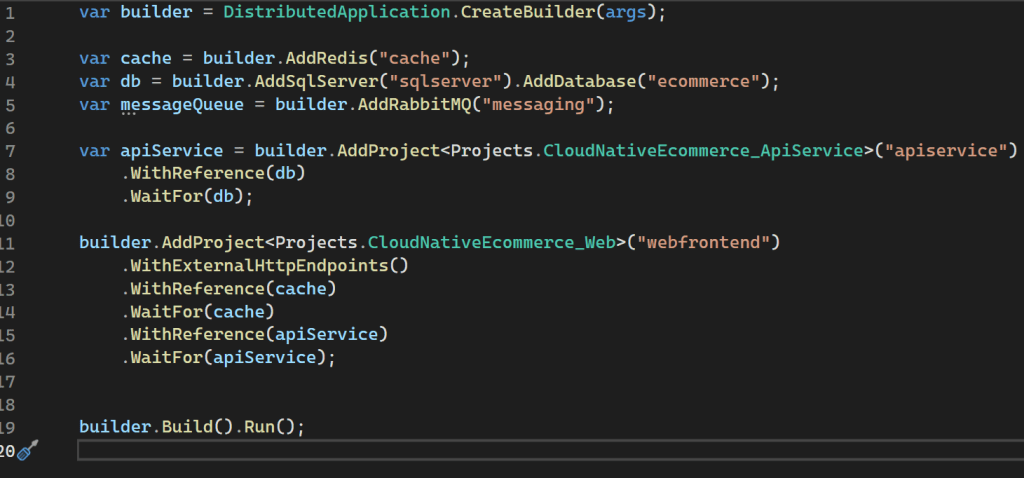
Simplifies SQL Server client registration within services without the need to manually configure any connection strings.

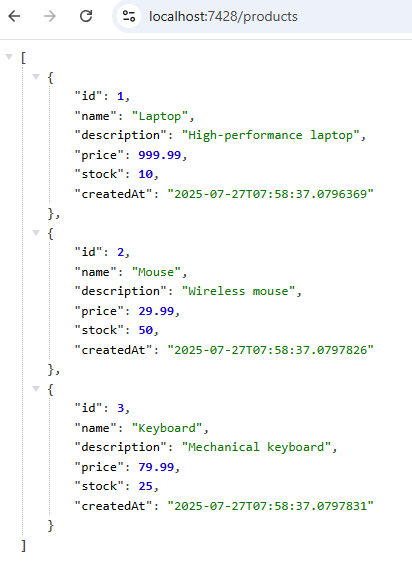
In the ApiService, I’ve created a Minimal API to retrieve all products—just a simple test to verify the SQL Server client integration. Now, let’s call the endpoint to confirm everything is working as expected.
2. Built-in Observability
Aspire automatically provides:
OpenTelemetry: Distributed tracing, metrics, logs
Integrated Dashboard: Real-time monitoring of all services
Structured Logging: Automatically aggregates logs from all services
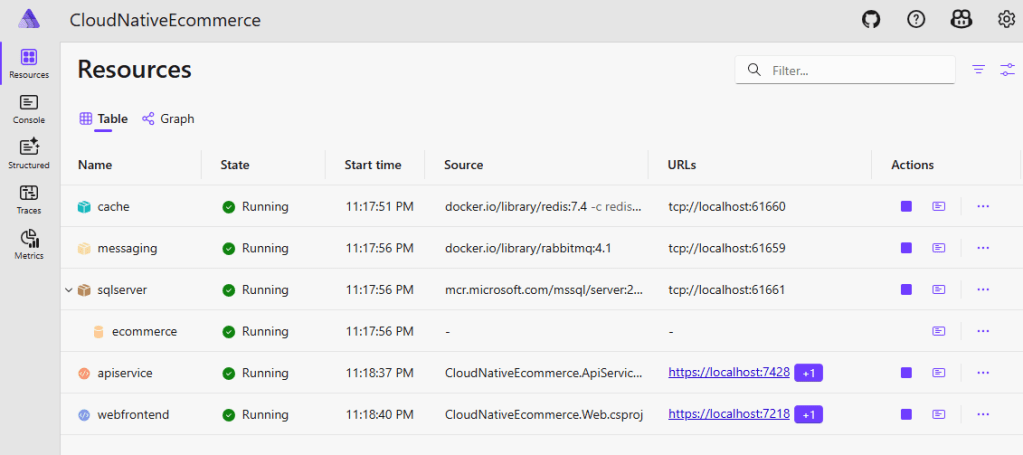
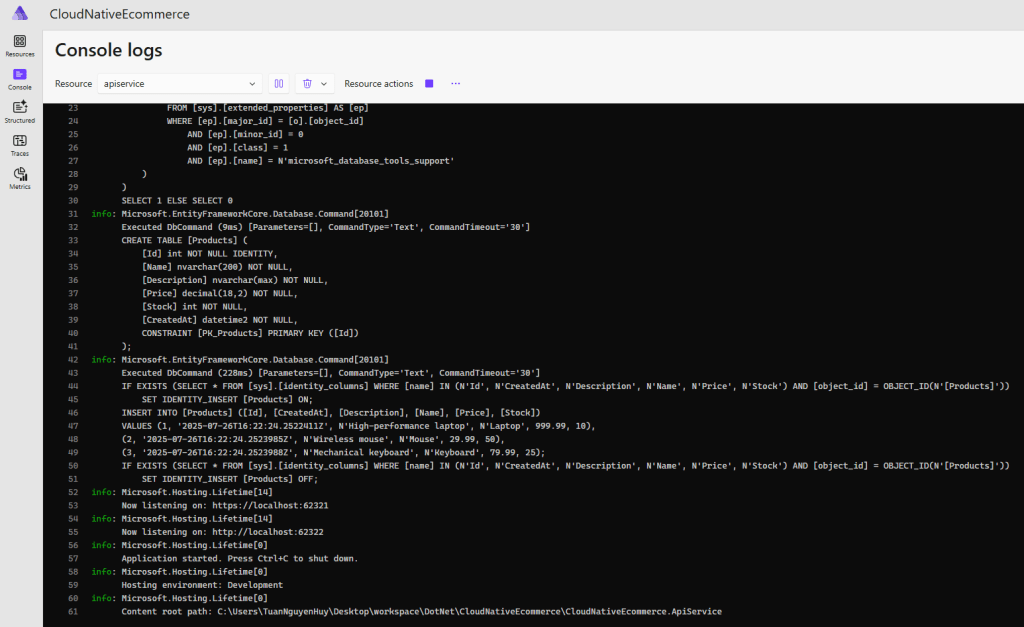
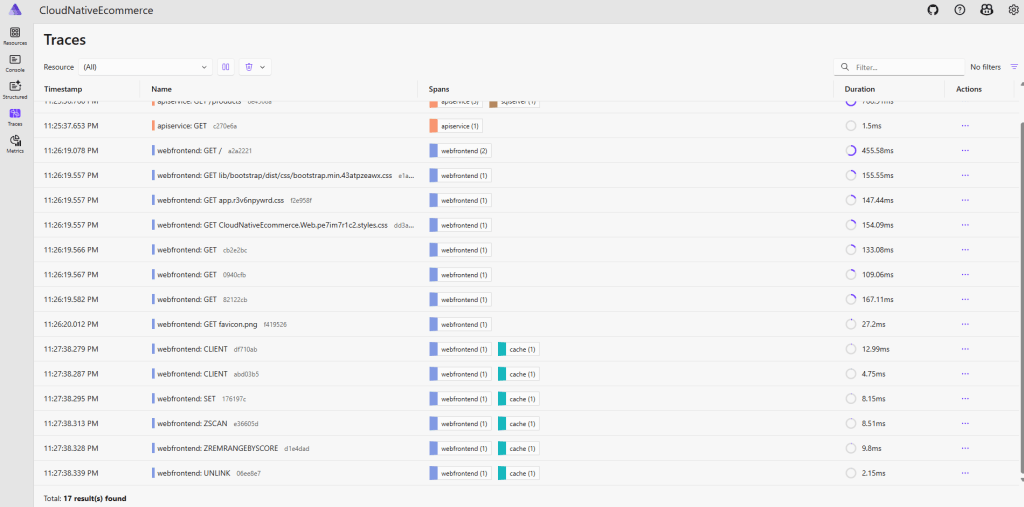
Aspire Dashboard displays:
Resource status of all services
Logs from any container
Request traces across services (ApiService & WebFrontend)
Metrics and performance data

3. Superior Development Experience
Hot Reload for entire stack: When you change code in one project, only that service is rebuilt and restarted, while other services continue running normally.
Unified Dashboard: A single interface to:
View logs from all services
Monitor resource usage
Trace request flow
Manage service lifecycle
Integrated Debugging: Can attach debugger to any service from Visual Studio.
4. Production-ready Deployment
Aspire can automatically generate:
- Docker Compose files for container deployment
- Kubernetes manifests for K8s deployment
- Azure Container Apps deployment files
For more details on deployment options, check out the official documentation:
Aspire Deployment Overview
You can also manually create a manifest to deploy on Kubernetes. I’ve already prepared one in the GitHub repository for demo. Now, let’s see how it runs on Kubernetes in action.
I won’t go into the details of Kubernetes or the deployment process in this post, so make sure you’re already familiar with K8s—or take some time to learn the basics before proceeding.
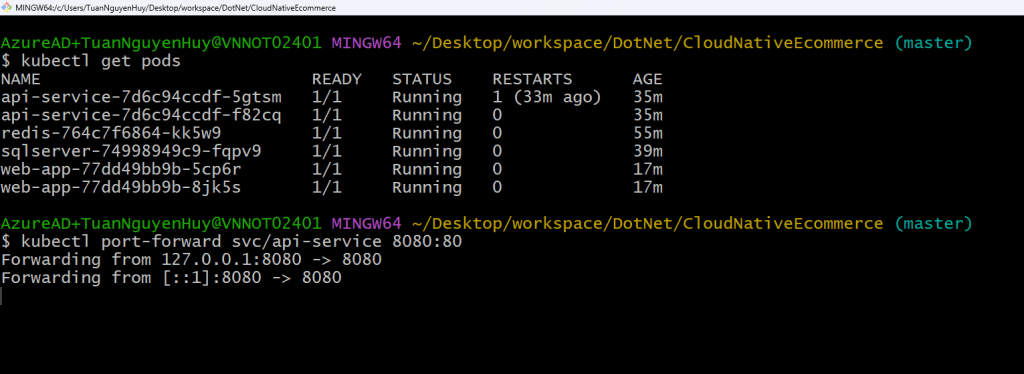
Now, let’s call the Get All Products API we created earlier and check if it’s working correctly.
You can use a tool like curl, Postman, or simply open the endpoint in your browser (if it’s a GET route) to verify the response.

The API running on Kubernetes returned the expected results—everything looks good! 🎉
Congratulations, your Aspire app is now up and running smoothly on K8s!
Conclusion
.NET Aspire offers a modern, opinionated approach to building cloud-native applications with .NET. From service discovery to built-in support for distributed infrastructure like SQL Server, Redis, and RabbitMQ, Aspire simplifies many of the complex tasks involved in microservice development.
In this post, we walked through creating an Aspire project, connected it to a SQL Server instance, and successfully deployed it to Kubernetes. While this is just the beginning, Aspire provides a strong foundation for scalable, production-ready systems.
Whether you’re building greenfield microservices or modernizing existing apps, Aspire is worth exploring.
Happy coding!

