1. What is Chrome Dev Tools Protocol (CDP)
Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP) is a remote debugging protocol (API). Chrome DevTools uses CDP to help you inspect the browser’s state, control its behavior, and collect debugging information. CDP provides a programmatic way to interact with the Chrome browser’s developer tools, allowing developers and testers to communicate with a running Chrome browser to control browser behavior, capture network requests, log console messages, monitor network traffic, and much more.
2. Selenium 4 Methods for CDP Interaction
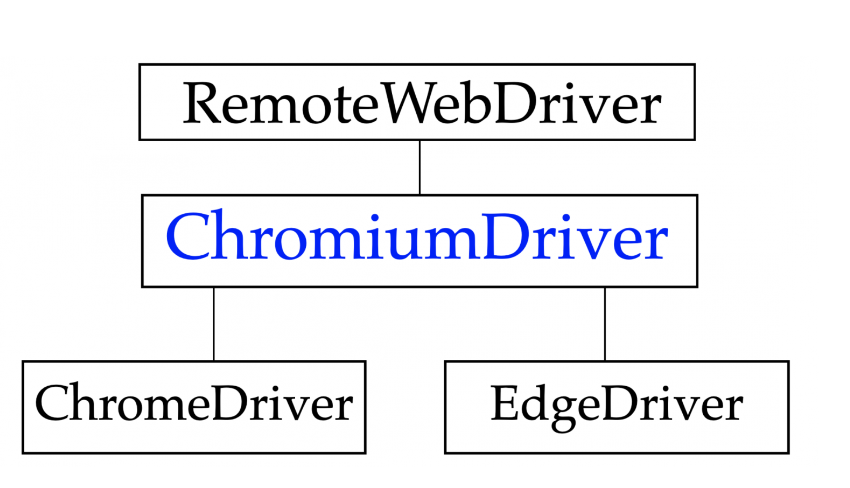
The Chromium-based drivers such as ChromeDriver and EdgeDriver now inherit from ChromiumDriver, so you also have access to the Selenium CDP APIs from these drivers as well. Selenium 4 introduces the new ChromiumDriver class, which includes two methods to access Chrome DevTools: GetDevToolsSession() and ExecuteCdpCommand().
- GetDevToolsSession() method creates a session to communicate with a browser using the Chromium Developer Tools debugging protocol. It returns DevToolsSession object that allows you to SendCommand() the built-in Selenium commands for CDP. These commands are wrapper methods that make it cleaner and easier to invoke CDP functions.
- ExecuteCdpCommand() method execute custom CDP commands with 2 params is command name and command parameters. For the valid CDP command name, let refer this document Chrome DevTools Protocol – Page domain.
3. How we can use CDP for Selenium 4 with C#
3.1. Capture HTTP Requests
using OpenQA.Selenium.Chrome;
using OpenQA.Selenium.DevTools;
using OpenQA.Selenium.DevTools.V130.Network;
DevToolsSession devToolsSession = ((ChromeDriver)driver).GetDevToolsSession();
var network = devToolsSession.GetVersionSpecificDomains <OpenQA.Selenium.DevTools.V130.DevToolsSessionDomains>().Network;
network.Enable(new EnableCommandSettings());
network.RequestWillBeSent += (sender, e) =>
{
if (e.Request.Url.Contains("selenium-4-chrome-devtools"))
{
Console.WriteLine($"Request URL: {e.Request.Url}");
Console.WriteLine($"Request Method: {e.Request.Method}");
if (e.Request.PostData != null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Request Post Data: {e.Request.PostData}");
}
}
};
network.ResponseReceived += (sender, e) =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Response URL: {e.Response.Url}");
Console.WriteLine($"Response Status: {e.Response.Status}");
};3.2. Simulate Device Mode
Nowadays most of the applications we build are responsive to meet to the needs of the end users coming from a variety of platforms, devices like phones, tablets, desktops and orientations. As automation testers, we might want to place our application in various dimensions to trigger the responsiveness of the application. CDP gives us a straightforward command to deal with it.
DevToolsSession devToolsSession = ((ChromeDriver)driver).GetDevToolsSession();
devToolsSession.Domains.Network.EnableNetwork();
((ChromeDriver)driver).ExecuteCdpCommand("Emulation.setDeviceMetricsOverride", new Dictionary<string, object>
{
["width"] = 1024,
["height"] = 1366,
["deviceScaleFactor"] = 1,
["mobile"] = true
});3.3. Simulate Network Throttling
Network Throttling is an intentional method to slow down the internet speed. It is used to analyze web performance where network throttling, or network condition emulation is used to emulate low bandwidth conditions. Network simulation helps developers or QAs simulate the performance of a website in different bandwidths like 2G, 3G, 4G, etc. This is extremely useful from a testing standpoint as testers get a sense of how the website loads and functions when accessed from different internet connections.
DevToolsSession devToolsSession = ((ChromeDriver)driver).GetDevToolsSession();
devToolsSession.Domains.Network.EnableNetwork();
var settings = new EmulateNetworkConditionsCommandSettings
{
Offline = false,
DownloadThroughput = 10,
UploadThroughput = 40,
Latency = 20,
ConnectionType = ConnectionType.Cellular2g //change to whatever connection type you want to emulate: 3g,4g...
};
devToolsSession.SendCommand(settings);3.4. Basic Authentication
Older ways to handle the Basic Authentication popup
- Passing username and password in the URL itself using following syntax:
https://username:password@your_website_url - Using Robot class with Keyboard key events.
- Using AutoIT.
- Chrome Dev Tool Protocol give another way to handle
DevToolsSession devToolsSession = ((ChromeDriver)driver).GetDevToolsSession();
devToolsSession.Domains.Network.EnableNetwork();
Headers headers = new Headers();
string basicAuth = "Basic " + Convert.ToBase64String(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(string.Format("{0}:{1}", "username", "password")));
headers.Add("Authorization", basicAuth);
devToolsSession.SendCommand(new SetExtraHTTPHeadersCommandSettings { Headers = headers });
3.5. Execute custom CDP command
Example to use CDP command to clear cookie
var driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.ExecuteCdpCommand("Storage.clearCookies", new Dictionary<string, object>());4. Conclusion
Selenium 4’s integration with the Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP) offers new opportunities for developers and testers. By utilizing CDP, you can programmatically control the Chrome browser, capture network requests, handle basic authentication, simulate Network speed, simulate Device mode and access browser information. As CDP continues to evolve, Selenium 4 provides a stable and convenient wrapper with the SendCommand() method for interacting with the Chrome DevTools Protocol, ensuring a seamless experience for automation testing.


