In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations increasingly rely on microservices architecture to create scalable, efficient, and resilient applications. Microservices allow businesses to develop and deploy applications as a suite of small, independent services that communicate over APIs. While this architectural style provides numerous advantages, it also presents unique challenges, especially around stability and reliability. This is where chaos testing comes into play—a method designed to ensure that your microservices can withstand unexpected disruptions and failures.
In this post, we will explore chaos testing in depth, discussing its principles, implementation, benefits, and best practices, specifically within the context of microservices architecture.
What is Chaos Testing
Chaos testing, also known as chaos engineering, is a discipline that focuses on intentionally injecting faults and failures into a system to observe how it behaves under stressful conditions. The primary goal is to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities, ensuring that systems can seamlessly recover from failures.
The concept of chaos testing stems from the necessity for systems to remain operational in the face of unpredictable failures—a crucial requirement for any microservices-based application. As microservices communicate with each other, the failure of one service can propagate to others, potentially causing widespread outages. Therefore, understanding how each component reacts under duress is paramount.
Importance of Chaos Testing in Microservices
Microservices architectures bring significant advantages, such as enhanced scalability, flexibility, and maintainability. However, they also introduce complexity and the potential for cascading failures. Here are several key reasons why chaos testing is particularly critical for microservices:
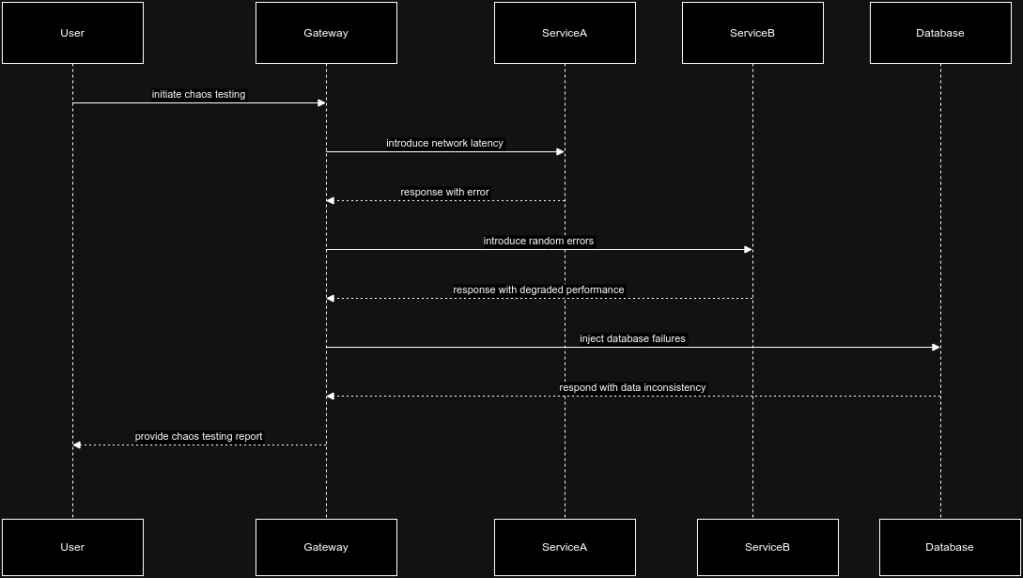
1. Identifying Single Points of Failure
With microservices architecture, failures can occur at any layer of the application stack. Chaos testing helps identify hidden vulnerabilities by simulating a wide range of failure scenarios, such as:
- Network partitioning
- Sudden service outages
- High latency
- Resource exhaustion
- API endpoint failures
By understanding how their microservices respond to these scenarios, organizations can take corrective actions to strengthen their systems.
2. Improving System Resilience
Chaos testing enhances the overall resilience and reliability of microservices. By actively testing how the system behaves when components fail, teams can refine their architecture and design to ensure that critical failures do not cascade through the application. This practice can lead to better fault tolerance, automatic failovers, and system recovery mechanisms, reducing the likelihood of service disruptions in production.
3. Validation of Recovery Mechanisms
The primary goal of chaos testing is not merely to identify failures but also to validate recovery mechanisms. In microservices architecture, services should be able to recover from failures automatically and continue functioning as expected. Through chaos testing, teams can test scenarios such as:
- Service restarts
- Rebooting containers
- Redistributing load
- Graceful degradation of capabilities
By validating these recovery processes, teams can ensure they are effective in real-world scenarios.
4. Encouraging a Culture of Proactive Thinking
Embracing chaos testing fosters a culture of proactive thinking among development and operations teams. Instead of adopting a reactive mindset focused solely on fixing issues after they arise, chaos testing encourages teams to anticipate failures and design their microservices with resilience in mind. This mindset shift can lead to more robust architecture and better incident response practices.
5. Enhancing Monitoring and Observability
Chaos testing helps improve monitoring and observability practices within microservices architecture. For teams to effectively respond to disruptions, they must have a clear understanding of how different services interact and the metrics that matter. By conducting chaos tests, organizations get to know where monitoring should be enhanced, leading to better observability strategies and a more comprehensive view of system health.
Challenges for Chaos Testing in Microservices

Successfully adopting chaos testing in a microservices environment involves several steps:
Challenge 1: Complexity of Inter-Service Communication
One of the primary challenges in chaos testing within microservices is the complexity of inter-service communication. Unlike monolithic applications, which operate as a single unit, microservices must communicate over a network using APIs. This adds a layer of complexity as various factors, such as network latency, service availability, and load balancing, can affect how services interact.
Mitigation Strategy
By decoupling the chaos testing framework from the business logic, teams can simulate different failure scenarios in a controlled manner, tracking how disruptions impact inter-service communications.
Challenge 2: Managing State and Data Consistency
Microservices often manage their own data and state, leading to concerns about data consistency when failures are introduced. In a system where each service is responsible for its data, simulating failures might lead to unexpected behaviours, such as data corruption or inconsistencies, particularly when cascading failures occur.
Mitigation Strategy
To effectively run chaos tests, it’s important to implement strategies such as event sourcing and distributed transaction patterns to manage state and data integrity across services. Using these patterns allows a microservices architecture to gracefully handle failures and roll back changes if necessary.
Challenge 3: Scale and Resource Management
Microservices applications can be composed of numerous services, each potentially experiencing chaos in different ways. The sheer number of components can result in scalability issues when conducting chaos tests. Simultaneously orchestrating multiple services to apply chaos can overwhelm the system, leading to performance bottlenecks that may skew test results.
Mitigation Strategy
Adopting a phased approach to chaos testing can ease resource constraints. Instead of storming the entire system with failures, organizations can introduce chaos incrementally, first targeting individual services and gradually scaling up to more complex scenarios.
Challenge 4: Creating Meaningful Metrics
Life in a microservices world often leads to a multitude of metrics. However, distinguishing which metrics matter for chaos testing poses its own challenges. With so many services interacting, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that are directly affected by chaos experiments is critical. Failure to do so might lead to ambiguous conclusions or misinterpretation of results.
Mitigation Strategy
Establish a clear set of success criteria and metrics before beginning any chaos experiment. Metrics should be selected based on business objectives, taking into account aspects such as error rates, response times, and user experience. Automated monitoring solutions can aid in collecting and displaying these metrics in real time, facilitating a quicker analysis of how systems respond to stress.
Challenge 5: Cultural Resistance
Despite the technical challenges associated with chaos testing, perhaps the most formidable obstacle lies within the organizational culture. Achieving a mindset that embraces failure as a means to improve resilience is often easier said than done. Teams may exhibit apprehension about breaking things in production, causing potential downtime or disruptions to clients.
Mitigation Strategy
Building a culture of trust and psychological safety is essential. Organizations can ease the transition into chaos engineering by conducting chaos experiments in a staging environment before moving to production. Providing training and workshops to illustrate the benefits of chaos testing will help install confidence across teams. Additionally, sharing success stories and lessons learned can motivate teams to embrace chaos engineering as a legitimate avenue for improvement.
Best Practices for Chaos Testing in Microservices
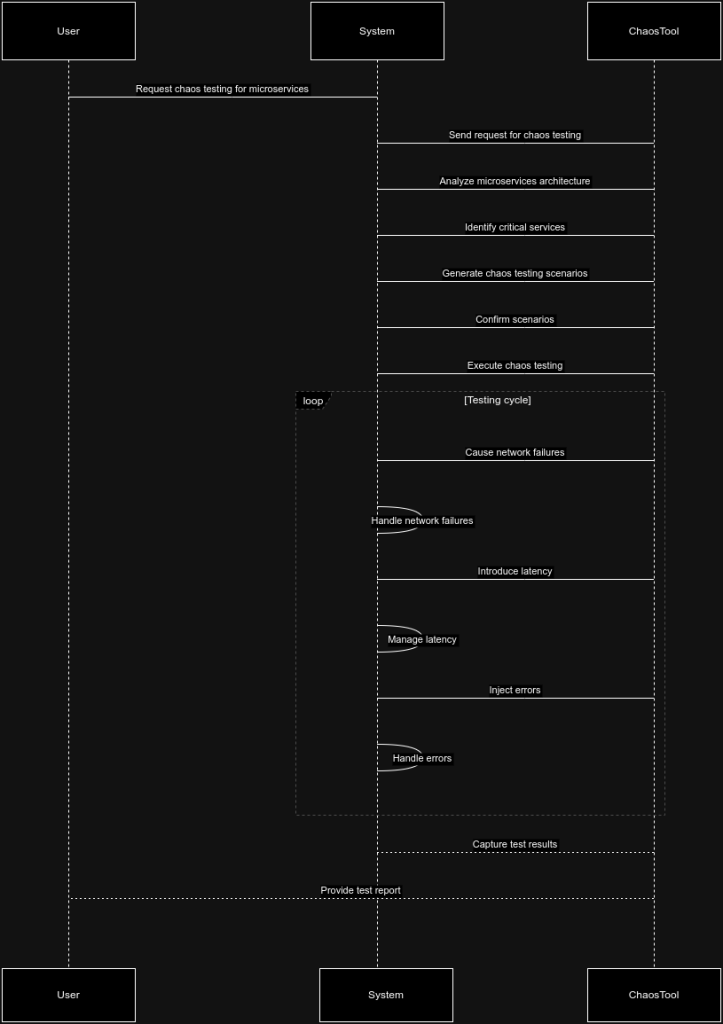
To maximize the benefits of chaos testing in microservices, consider the following best practices:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before embarking on chaos testing, it is essential to define clear objectives. What do you want to achieve from chaos testing? Common goals include assessing system resiliency, understanding failure modes, and validating recovery processes.
2. Start Small and Simple
When you first introduce chaos testing into your microservices architecture, it’s best to start small. Begin with simple experiments that involve controlled disruptions, such as terminating a single service or introducing latency in API calls. As you gain confidence and experience, gradually progress to more complex scenarios that involve multiple services, or even simulate larger-scale failures.
3. Use Feature Flags and Automation
Leverage feature flags to control chaos experiments in production environments. Feature flags allow you to turn chaos tests on and off, providing a safety net to revert changes if necessary. Additionally, automate the deployment of chaos experiments using orchestration tools to streamline the process, minimize manual intervention, and reduce the likelihood of human errors.
4. Monitor and Measure
Effective monitoring and measurement are crucial for chaos testing success. Implement robust observability practices to gather metrics about your services, such as response times, error rates, and resource utilization. Utilize monitoring tools that can dynamically ingest and visualize this data in real time, allowing you to assess the impact of chaos experiments quickly. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate your system’s performance during and after the chaos tests.
5. Implement Gradual Ramp-Ups
Avoid overwhelming the system with sudden disruptions. Instead, implement gradual ramp-ups in chaos engineering experiments to incrementally increase the failure load. This approach allows your systems to adjust and helps teams to observe how small increases in failure impact the overall performance and stability. By starting with a controlled level of chaos, you can gain valuable insights without inducing catastrophic failures.
6. Ensure Comprehensive Documentation
Document every chaos engineering experiment, including the hypothesis, the executed tests, and the outcomes. Comprehensive documentation helps to create a knowledge base for your organization, making it easier for teams to learn from past experiments and replicate successful tests in the future. Additionally, maintaining a clear record of experiments can facilitate discussions around system improvements.
7. Simulate Real-World Scenarios
To maximize the effectiveness of your chaos tests, simulate real-world scenarios that could impact your microservices. Consider factors like network partitioning, resource starvation, and varying user loads. By closely mimicking potential outages and failures, you can gain more accurate insights into how your architecture will perform under stress and identify the true limits of your system.
8. Prepare for Rollbacks and Recovery
Have rollback and recovery plans in place before conducting chaos experiments. Ensure your teams know how to revert any disruptions or failures caused by chaos testing. Regularly update your recovery mechanisms based on the outcomes of your experiments to improve response strategies and minimize recovery times after incidents.
References
- Mastering Chaos – A Netflix guide to Microservices
- Chaos Monkey testing with Microservices
- Chaos Testing your HTTP Microservices


