Cloud testing platforms are extremely important in web and mobile development. These platforms are important resources for developers, allowing them to extensively test the performance of their websites and mobile apps. These testing platforms reduce the need for users to install virtual computers, devices, or emulators by giving access to on-demand browsers, several operating systems, and a wide range of mobile devices. In the automated testing field, moving test execution to the cloud makes automated testing of web applications independent of physical infrastructure. This eliminates the need to acquire and maintain devices for testing.. A Selenium cloud also provides high availability which reduces the risk of downtime.There are many providers of this service in the market such as Browserstack, SauceLabs, LambdaTest and so on. In this post, I will show you how to run automation test scripts on AWS Device Farm, a cloud testing platform from the AWS ecosystem.
AWS Device Farm
AWS Device Farm is an application testing service that lets you improve the quality of your web and mobile apps by testing them across an extensive range of desktop browsers and real mobile devices; without having to provision and manage any testing infrastructure. The service enables you to run your tests concurrently on multiple desktop browsers or real devices to speed up the execution of your test suite, and generates videos and logs to help you quickly identify issues with your app. 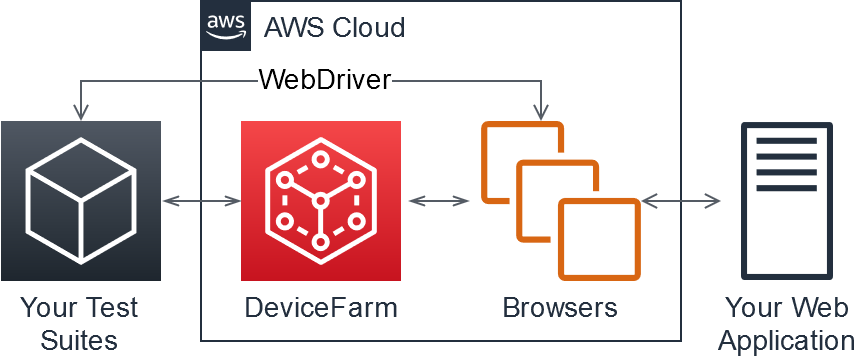
What is Selenium?
Selenium refers to a suite of tools that are widely used in the testing community when it comes to cross-browser testing. Selenium cannot automate desktop applications; it can only be used in browsers. It is considered to be one of the most preferred tool suites for automation testing of web applications as it provides support for popular web browsers which makes it very powerful. It supports a number of browsers (Google Chrome 12+, Internet Explorer 7,8,9,10, Safari 5.1+, Opera 11.5, Firefox 3+) and operating systems (Windows, Mac, Linux/Unix). Selenium also provides compatibility with different programming languages – C#, Java, JavaScript, Ruby, Python, PHP. Testers can choose which language to design test cases in, thus making Selenium highly favorable for its flexibility. Note: It is not mandatory to write Selenium code in the same language as the application. For example, if the application under test is written in PHP, then testers don’t have to write Selenium code in PHP. Thus, if a website is written in C#, the Selenium code can be written in PHP too.
Steps to execute the test on AWS Device Farm
1. Setup AWS Authentication
-
Install AWS CLI https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html
-
Create AWS Access Key https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_root-user_manage_add-key.html
- After installing AWS CLI you need to configure your account with command
aws configure
- You need to add the following credentials:
- AWS Access Key ID
- AWS Secret Access Key
- Default region name – for example us-west-2
2. Create AWS Device Farm Project
- Sign in to the Device Farm console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/devicefarm.

- Click Next to start creating a new project.
- In the navigation pane, choose Desktop Browser Testing, and then choose Projects.

- If you already have a project, under Desktop browser testing projects, choose the name of your project.Otherwise, to create a new project, choose New project. Then, on the Create Project page, do the following:
- Enter a Project name.
- (Optional) Enter a project Description.
- (Optional) Under Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Settings, you can configure your project’s VPC peering settings by choosing the VPC, its Subnets, and its Security Groups. For instructions on connecting Device Farm to a VPC, see Working with Amazon Virtual Private Cloud across Regions in the Device Farm Developer Guide.
- Choose Create.
- In the project details, note the project’s Amazon Resource Name (ARN). It looks like this: arn:aws:devicefarm:us-west-2:716996374103:testgrid-project:000c45a5-3e42-45fa-80c7-e99493c92672.
3. Prepare the Selenium Project
- Open Eclipse, create a Maven project and named it as SeleniumAWSDeviceFarm
- Add the following maven dependencies in the POM.xml file
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> <artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId> <version>4.1.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>software.amazon.awssdk</groupId> <artifactId>aws-sdk-java</artifactId> <version>2.10.60</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.testng</groupId> <artifactId>testng</artifactId> <version>7.1.0</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
- The full code of example:
package demo.SeleniumAWSDeviceFarm;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import software.amazon.awssdk.regions.Region;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.devicefarm.*;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.devicefarm.model.*;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class AppTest {
private static RemoteWebDriver driver;
@BeforeTest
void setUp() {
String myProjectARN = "arn:aws:devicefarm:us-west-2:716996374103:testgrid-project:000c45a5-3e42-45fa-80c7-e99493c92672";
DeviceFarmClient client = DeviceFarmClient.builder().region(Region.US_WEST_2).build();
CreateTestGridUrlRequest request = CreateTestGridUrlRequest.builder().expiresInSeconds(300)
.projectArn(myProjectARN).build();
CreateTestGridUrlResponse response = client.createTestGridUrl(request);
URL testGridUrl = null;
try {
testGridUrl = new URL(response.url());
ChromeOptions options = new ChromeOptions();
options.addArguments("disable-infobars");
options.setAcceptInsecureCerts(true);
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(testGridUrl, options);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void googleSearch() {
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.navigate().to("https://www.google.com/");
driver.findElement(By.name("q")).sendKeys("AWS DeviceFarm");
driver.findElement(By.name("btnK")).click();
}
@AfterTest
void tearDown() {
driver.quit();
}
}
4. Execute the Test
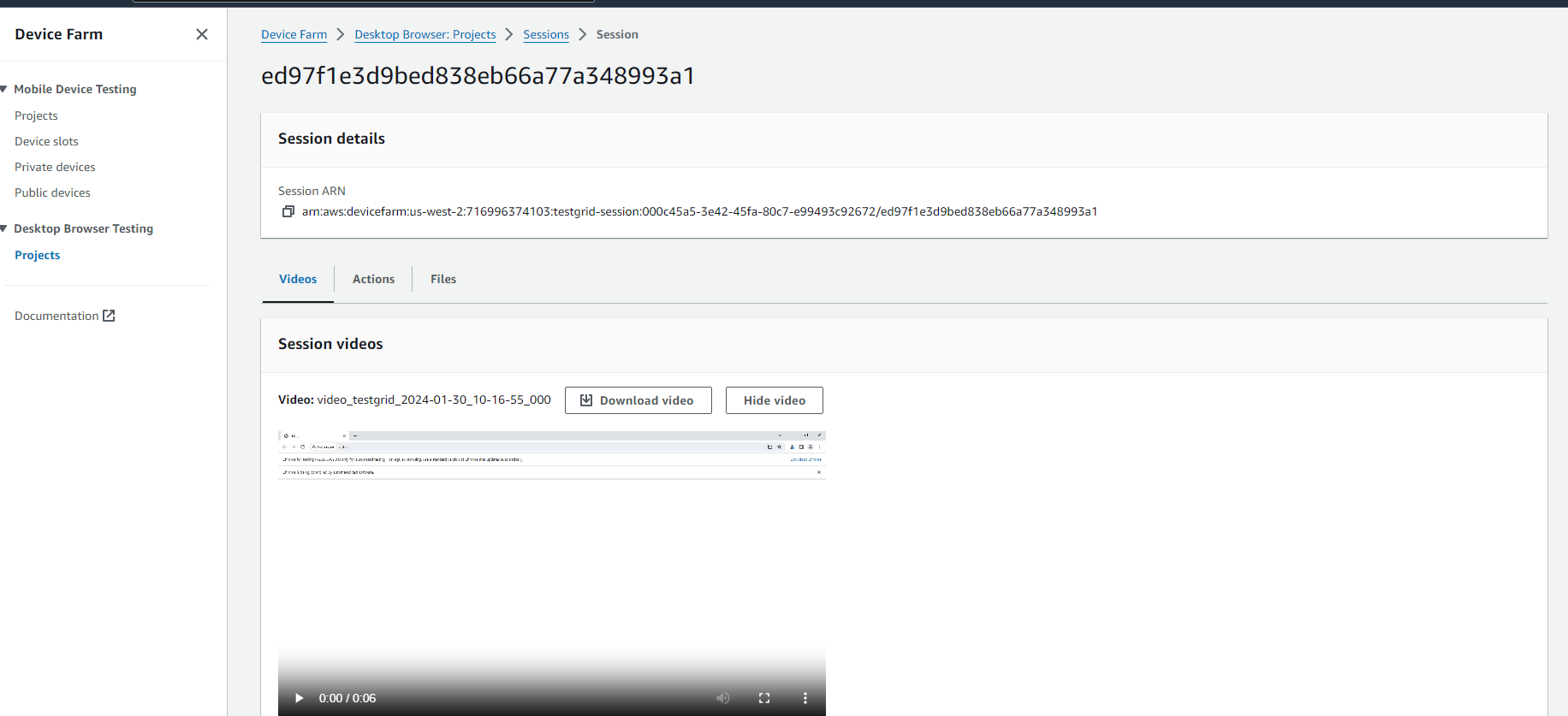
- Run a test to verify the configuration is successful. If the configuration is correct, a session ID will be generated at the Sessions panel of AWS Device Farm project.

- Click on session ID, we can view or download video recording of the automation test execution on the browser.