API security is a critical aspect of modern software development, ensuring that applications remain resilient against a wide array of potential vulnerabilities. One of the most effective techniques for uncovering hidden bugs and vulnerabilities in APIs is fuzzing. This blog delves into the techniques and tools used in fuzzing for API security testing, and provides practical examples of creating custom fuzzers for RESTful APIs using tools such as FuzzAPI and Boofuzz.
What is Fuzzing?
Fuzzing, sometimes known as fuzz testing, is an automated software testing method in which erroneous, unexpected, or random data is fed into a computer program. The primary goal is to discover security vulnerabilities and bugs by observing how the program behaves when it processes these inputs. Fuzzing can reveal issues such as crashes, memory leaks, and assertion failures.
Modern Fuzzing Techniques for APIs
Modern fuzzing techniques for APIs have evolved to address the complexity and diversity of API endpoints. These techniques include:
- Mutation-Based Fuzzing: This involves altering existing inputs (requests) to create new test cases. It’s effective for exploring variations of known valid inputs.
- FuzzAPI: A dedicated tool for fuzzing RESTful APIs.
- Generation-Based Fuzzing: This involves creating entirely new inputs from scratch based on the API specification. This technique is useful for exploring inputs that are valid according to the specification but have not been explicitly tested.
- Boofuzz: An open-source network protocol fuzzing tool.
- Stateful Fuzzing: This approach maintains the state between different API calls, ensuring that the sequence of calls respects the stateful nature of the API.
- Feedback-Driven Fuzzing: This technique uses feedback from the API’s responses to guide the fuzzing process, allowing for more intelligent exploration of the input space.
- Atheris: A fast and efficient fuzzer for Python applications.
Tools for API Fuzzing
Several tools are available for fuzzing APIs, each offering unique features and capabilities. Below are two prominent tools: FuzzAPI and Boofuzz.
FuzzAPI
FuzzAPI is an open-source tool designed specifically for fuzzing RESTful APIs. It provides a user-friendly interface and supports both mutation-based and generation-based fuzzing.
Key Features of FuzzAPI:
- Automatic discovery of API endpoints.
- Support for custom payloads and headers.
- Logging and reporting of fuzzing results.
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing.
Example of Using FuzzAPI:
FuzzAPI is a simple yet powerful tool designed to fuzz RESTful APIs. In this example, we will demonstrate how to use FuzzAPI to fuzz endpoints on the https://reqres.in/ API.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fuzzing with FuzzAPI
Step 1: Install FuzzAPI
First, ensure you have Python installed on your system. You can download it from python.org.
Next, install the necessary dependencies for FuzzAPI.
pip install requestsStep 2: Create the Fuzzing Script
Create a Python script named api_fuzzer.py. This script will define the endpoints and the parameters we want to fuzz.
import requests
import random
import string
# Define the API's base URL.
base_url = "https://reqres.in/api"
# Function to generate random strings
def random_string(length=8):
letters = string.ascii_lowercase
return ''.join(random.choice(letters) for i in range(length))
# Function to fuzz GET /users endpoint
def fuzz_users_get():
endpoint = f"{base_url}/users"
params = {"page": random_string()}
response = requests.get(endpoint, params=params)
print(f"Fuzzed GET {endpoint}")
print(f"Response Code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response Body: {response.text}\n")
# Function to fuzz POST /users endpoint
def fuzz_users_post():
endpoint = f"{base_url}/users"
data = {"name": random_string(), "job": random_string()}
response = requests.post(endpoint, json=data)
print(f"Fuzzed POST {endpoint}")
print(f"Response Code: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response Body: {response.text}\n")
# Main function to run fuzzing
def main():
fuzz_users_get()
fuzz_users_post()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Step 3: Run the Fuzzing Script
Execute your script using Python.
python3 api_fuzzer.pyThis script will randomly generate parameters for the GET /users and POST /users endpoints of the ReqRes API, send the requests, and print out the responses.
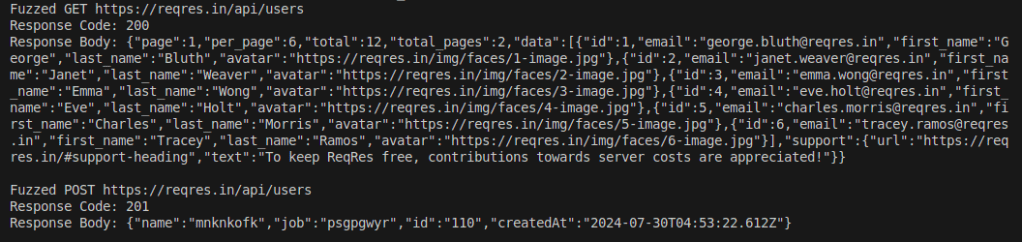
Step 4: Output
The following output should appear when the script is executed:
Boofuzz
Boofuzz is a powerful and flexible fuzzing framework written in Python. It is a fork of the popular Sulley framework and is designed for fuzzing network protocols, file formats, and APIs.
Key Features of Boofuzz:
- Modular architecture for extensibility.
- Ability to fuzz different types of inputs.
- Real-time monitoring and logging.
- Support for complex, stateful protocols.
Example of Creating a Custom Fuzzer with Boofuzz:
Boofuzz is a powerful and flexible fuzzing tool primarily designed for network protocol fuzzing, but it can be adapted for fuzzing RESTful APIs. Below, we’ll demonstrate how to use Boofuzz to fuzz endpoints on the https://reqres.in/ API.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fuzzing with Boofuzz
Step 1: Install Boofuzz
First, install Boofuzz and its dependencies:
pip install boofuzzStep 2: Create the Fuzzing Script
Create a script named fuzzing_script.py with the following content:
from boofuzz import *
import requests
def fuzz_users_get(session):
s_initialize("GET /users")
with s_block("Request-Line"):
s_static("GET /api/users?")
s_delim("&")
s_string("page")
s_delim("=")
s_string("1")
s_static(" HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: reqres.in\r\n\r\n")
session.connect(s_get("GET /users"))
session.fuzz()
def fuzz_users_post(session):
s_initialize("POST /users")
with s_block("Request-Line"):
s_static("POST /api/users HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: reqres.in\r\nContent-Type: application/json\r\n\r\n")
s_static("{\"name\": \"")
s_string("user")
s_static("\", \"job\": \"")
s_string("leader")
s_static("\"}")
session.connect(s_get("POST /users"))
session.fuzz()
def main():
session = Session(
target=Target(connection=SocketConnection("reqres.in", 80, proto='tcp')),
sleep_time=1,
web_port=26000 # Starts the web interface on port 26000
)
fuzz_users_get(session)
fuzz_users_post(session)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Step 3: Run the Fuzzing Script
Execute the script to start fuzzing the API endpoints:
python3 fuzzing_script.py
Step 4: Output
The script will start fuzzing the GET /api/users and POST /api/users endpoints on https://reqres.in. You will see the fuzzing progress in the console. Additionally, you can access the web interface for Boofuzz at http://localhost:26000 to monitor and control the fuzzing process.
The fuzzing process initiated by the script will run until it exhausts all possible permutations of the input.

Conclusion
Fuzzing is an essential technique for ensuring the security and robustness of APIs. By leveraging tools like FuzzAPI and Boofuzz, developers and security testers can automate the process of discovering vulnerabilities and improving the resilience of their APIs. With continuous advancements in fuzzing techniques, the ability to uncover and mitigate potential security risks in APIs will only improve, making fuzzing a critical component of modern API security testing.