Insomnia’s is an open-source API testing platform that provides a user-friendly interface, making it easy to create and manage API requests. Whether you’re testing REST, GraphQL, or SOAP APIs, Insomnia’s offers a clean and intuitive workspace to design, debug, and share your API requests. It’s an excellent option for both developers and testers due to its vast feature set, adaptability, and vibrant community.
INSOMNIA’S ROLE IN API TESTING
Insomnia plays a significant role in API testing by providing developers and testers with a powerful platform to design, execute, and manage tests for Apis. It serves as a versatile and efficient tool for API testing, offering a wide range of features to streamline the testing process and ensure the quality and reliability of APIs.
Here are some of the ways in which Insomnia contributes to API testing:
Request Creation:
Users can generate a variety of HTTP requests (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) with customisable headers, arguments, and payloads with ease using Insomnia. This makes it possible for testers to model various API interactions and scenarios.
Environment Management:
Insomnia supports the creation of multiple environments, allowing testers to define variables for different environments (e.g., development, staging, production). This facilitates testing in different contexts and ensures that tests can be easily adapted for various environments.
Dynamic Variables:
Insomnia supports dynamic variables that can be used to generate values dynamically during test execution. This feature is useful for creating dynamic payloads, generating unique identifiers, or extracting data from responses to use in subsequent requests.
Authentication:
Insomnia supports various authentication methods commonly used in APIs, such as Basic Auth, OAuth, API keys, and JWT tokens. Testers can easily configure authentication settings for requests, allowing them to simulate authenticated API interactions.
Response Validation:
Insomnia provides tools for validating API responses, including status codes, headers, and response bodies. Testers can define assertions to verify that the API responses meet the expected criteria, ensuring correctness and consistency.
Scripting:
Insomnia allows users to write custom scripts (using JavaScript) to manipulate request parameters, extract data from responses, or perform advanced validation logic. This flexibility enables testers to implement complex testing scenarios and automate repetitive tasks.
Test Automation:
Insomnia supports test automation through the use of collections and environments, which can be exported and executed using command-line tools or integrated into continuous integration (CI) pipelines. This allows testers to automate the execution of API tests and incorporate them into their development workflows.
Collaboration and Sharing:
Insomnia provides features for sharing workspaces, collections, and environments with team members, facilitating collaboration on API testing efforts. Testers can easily share their test configurations and results, improving communication and coordination within the team.
INSOMNIA’S ARCHITECTURE
The architecture of Insomnia is well-structured, allowing it to handle HTTP requests, responses, and different testing scenarios efficiently. This makes Insomnia an excellent tool for testing APIs. Its functionalities and characteristics form the basis of its architecture.
User Interface (UI):
The front-end component of Insomnia comprises the user interface, where testers interact with the application. The UI is responsible for rendering the various elements of Insomnia, such as request builders, response viewers, and configuration settings.
Request Builder:
The Request Builder module, which enables testers to create HTTP requests, is the central component of Insomnia’s architecture. This module provides an easy-to-use interface for specifying request methods, headers, parameters, and payloads. The request builder probably contains of input fields to add headers, query parameters, request body, etc., and components to handle various request types (e.g., GET, POST, PUT).
Execution Engine:
Insomnia includes an execution engine responsible for sending HTTP requests to the specified endpoints and processing the corresponding responses. This engine handles the actual communication with the API under test. The execution engine may utilise libraries or modules for making HTTP requests, handling authentication, managing cookies, and dealing with various response formats like JSON, XML, etc.
Environment Management:
Insomnia allows testers to define and manage environment variables, which facilitate configuration management across different testing environments. This component handles the storage and retrieval of environment variables and their substitution in requests. Environment management likely involves storing environment data in a structured format (e.g., JSON) and providing mechanisms for testers to switch between different environments seamlessly.
Workspace Management:
Insomnia organises testing projects into workspaces, providing a centralized hub for collaboration and management. This component handles the creation, deletion, and navigation of workspaces, as well as the storage of workspace-related data.
Workspace management may involve file system operations for storing workspace files, metadata management for tracking workspace properties, and user interface components for displaying workspace contents.
Plugins and Extensions:
Insomnia offers a rich ecosystem of plugins and extensions that extend its functionality and adaptability. This component provides an interface for loading, activating, and managing plugins within the Insomnia environment. Plugin management likely involves mechanisms for discovering, installing, and updating plugins, as well as providing APIs or hooks for plugins to integrate with Insomnia’s core functionalities.
INSOMNIA’S WORKFLOW
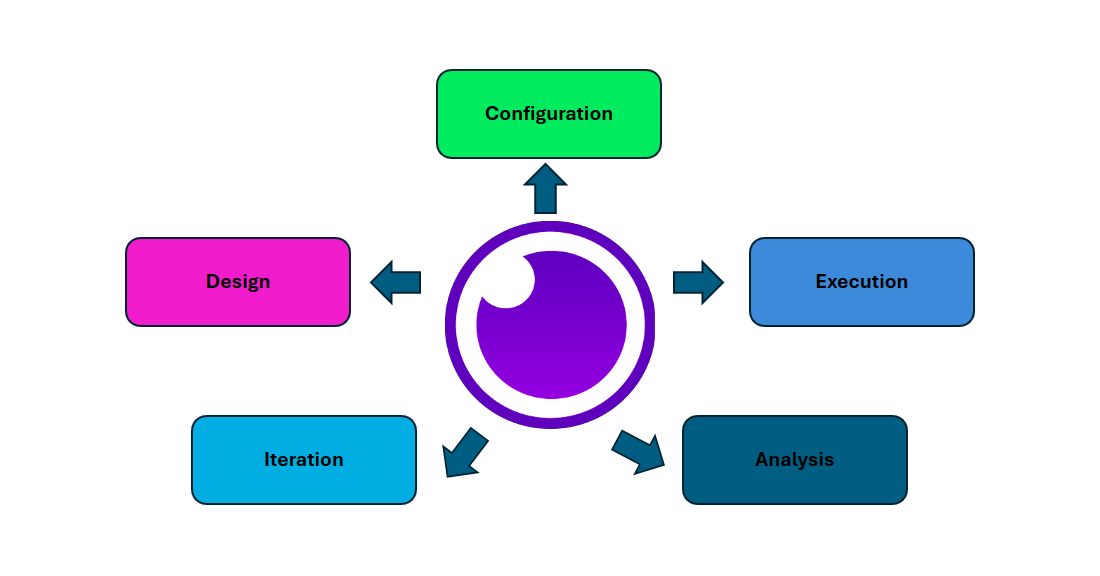
The workflow used by Insomnia consists of a number of iterative procedures meant to achieve comprehensive API testing. The following steps are usually included in the workflow:
Design:
Using the user-friendly interface of Insomnia, testers sketch out the API specifications and endpoints during this stage. They establish request parameters, payloads, and methods, setting the stage for further testing.
Configuration:
Testers configure Insomnia settings and environment variables to align with the testing environment. This step ensures consistency and accuracy across test runs, minimising discrepancies and errors.
Execution:
Testers run test cases in Insomnia’s environment after setting up the API endpoints and configurations. They make requests, examine answers, and compare the behaviour of the API to what is anticipated.
Analysis:
Testers can examine response data, monitor performance metrics, and spot irregularities with the help of Insomnia’s extensive result analysis tools. To guarantee the functionality and dependability of the API, testers make use of built-in features like response validation and status code verification.
Iteration:
Testing is an iterative process, and Insomnia facilitates seamless iteration through its collaborative features and version control capabilities. Testers can refine test cases, address issues, and incorporate feedback iteratively, ensuring continuous improvement of the API’s quality.

Insomnia empowers testers with its intuitive interface, robust features, and seamless integration, facilitating efficient API testing from design to execution in several ways:
Efficient Request Building:
Insomnia offers an intuitive interface for building HTTP requests, allowing testers to easily specify request methods, headers, parameters, and payloads. This streamlined process accelerates the creation of test cases, saving time and effort for testers.
Comprehensive Testing Features:
Insomnia provides a wide range of testing features to accommodate different testing scenarios. Testers can perform various types of tests, including functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and more, using Insomnia’s built-in tools and functionalities.
Flexibility with Environment Variables:
Insomnia allows testers to define and manage environment variables, enabling them to configure and customise test environments easily. This flexibility is especially beneficial when testing across multiple environments or configurations, as testers can switch between setups seamlessly.
Advanced Validation and Assertions:
Insomnia supports advanced validation and assertion capabilities, allowing testers to verify API responses against expected outcomes with precision. Testers can define validation rules, such as checking response status codes, headers, or response body contents, to ensure API correctness and reliability.
Collaborative Workspaces:
Insomnia facilitates collaboration among testers through its shared workspaces feature. Testers can collaborate on testing projects in real-time, share test cases, and provide feedback, fostering teamwork and enhancing productivity.
Extensibility via Plugins:
Insomnia’s plugin system enables testers to extend its functionality according to their specific requirements. Testers can install plugins to integrate with other tools, customise workflows, or add additional features, enhancing Insomnia’s capabilities to suit their testing needs.
Integration with Development Workflow:
Insomnia seamlessly integrates with version control systems like Git, enabling testers to manage and version their API test suites alongside their application code. This integration ensures alignment between development and testing efforts, promoting consistency and collaboration.
Detailed Result Analysis:
Insomnia provides comprehensive tools for analysing test results, including detailed response data, performance metrics, and error logs. Testers can easily identify and troubleshoot issues, track testing progress, and make informed decisions based on insightful analytics.
Example:
Let’s say you want to test an API endpoint that retrieves information about a user. Here’s how you would set it up in Insomnia:
1. Open Insomnia: Open the Insomnia application on your computer.
2. Create a New Request:
- Click on the “+ New Request” button in the top-left corner.
- Give your request a name, like “Get User Info”.

3. Set Request Details:
- In the URL field, enter the endpoint URL of the API you want to test. For example: https://reqres.in/api/users?page=2
- Choose the HTTP method as “GET” from the dropdown menu.
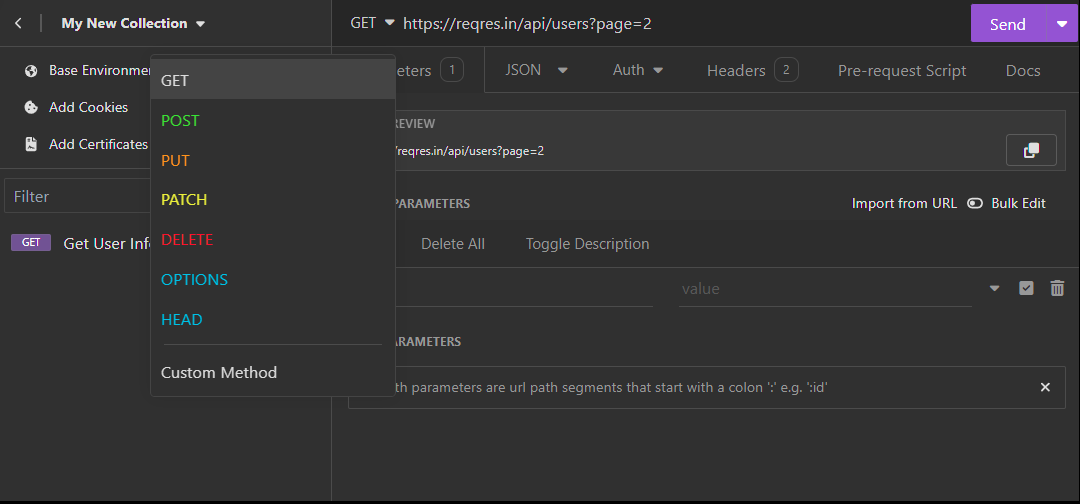
4. Add Headers (Optional):
- If your API requires specific headers, you can add them under the “Headers” section by clicking on “Add Header”. For example, you might add an Authorization header if the API requires authentication.

5. Send the Request:
- Once you’ve set up your request, click the “Send” button to execute it.
6. View Response:
- Insomnia will show you the response in the “Response” section.
- You’ll see the status code, headers, and response body.
- If the response is in JSON format, Insomnia provides a formatted view for better readability.
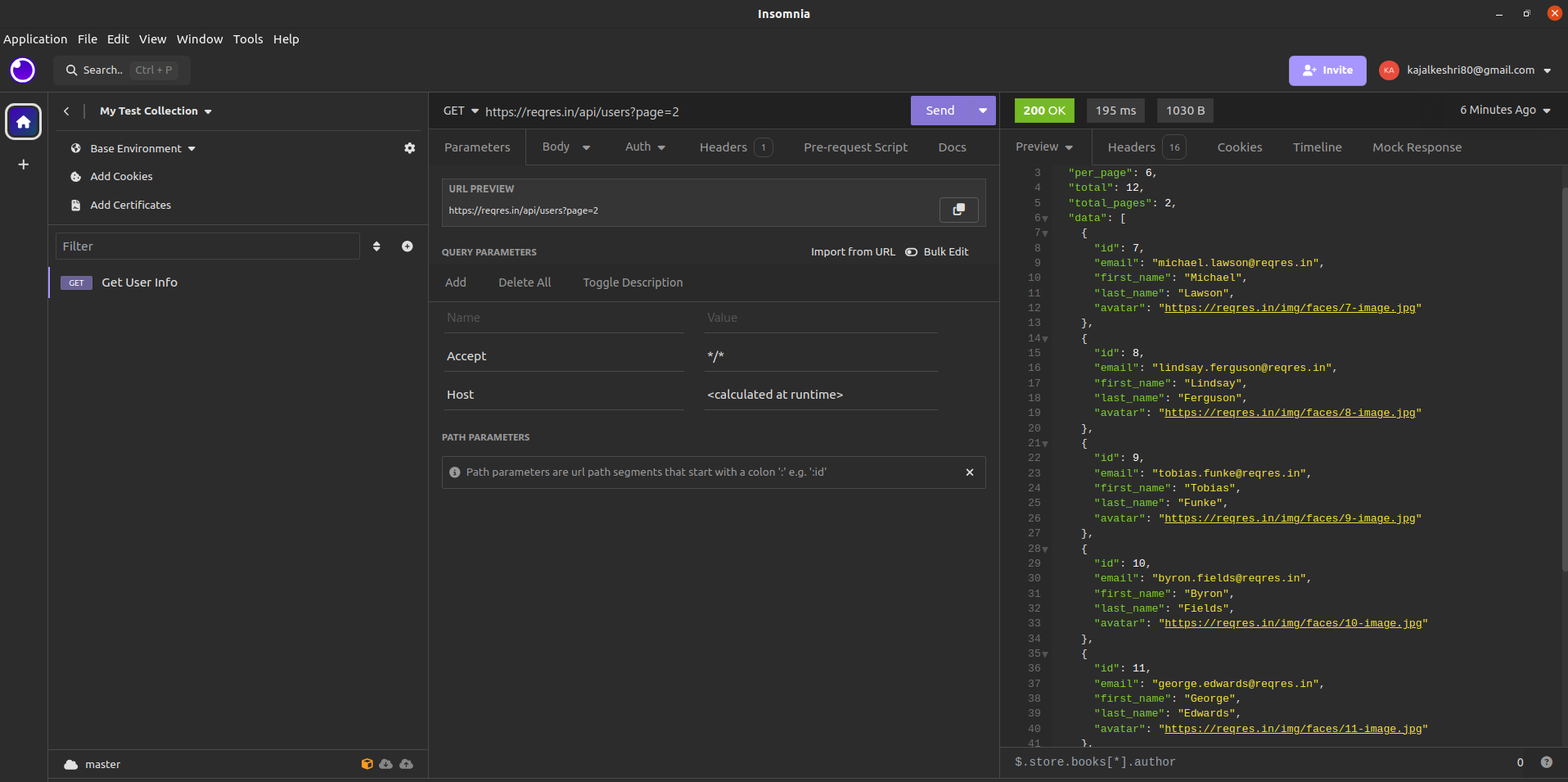
That’s it! You’ve now hit a request in the Insomnia tool and viewed the response. You can repeat these steps for testing different endpoints or scenarios. Insomnia also provides various features like environments, workspaces, and collections to organize and manage your requests effectively.
HOW INSOMNIA IS DIFFERENT FROM OTHER API TESTING TOOLS LIKE POSTMAN
Insomnia and Postman are both popular API testing tools, but they have several differences in terms of features, user interface, and capabilities. Here are some key differences between Insomnia and Postman:
- User Interface (UI): Insomnia has a more modern and minimalistic UI compared to Postman. Insomnia’s UI is designed to be more intuitive and clutter-free, which can make it easier to navigate for some users.
- Open-Source: Insomnia is an open-source tool, while Postman has a free version but also offers paid plans with additional features. This makes Insomnia more accessible for developers who prefer open-source software or have limited budgets.
- Plugins and Customization: Insomnia has a more robust plugin ecosystem, allowing developers to extend its functionality and customize it to their specific needs. Postman also has plugins, but Insomnia’s plugin ecosystem is generally considered more extensive.
- GraphQL Support: Insomnia has built-in support for GraphQL, which includes features like GraphQL query autocomplete, query validation, and response rendering. Postman also supports GraphQL, but its GraphQL features are not as extensive as Insomnia’s.
- Design and Documentation: Insomnia offers better design and documentation capabilities compared to Postman. Insomnia allows developers to design and document their APIs within the tool, making it easier to collaborate and share API documentation with team members or clients.
- Environment and Data Management: Both tools offer environment and data management features, but some developers find Insomnia’s approach more intuitive and easier to work with, particularly for managing multiple environments and data files.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: While both tools are available for multiple platforms, Insomnia has a web-based version (Insomnia Inso Cloud) that can be accessed from any device with a web browser, making it more portable and accessible.
- Performance: Some users have reported that Insomnia performs better than Postman, especially when dealing with large API responses or when working with a large number of requests and collections.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, Insomnia emerges as a powerful tool for testers in API testing, offering a host of features and capabilities that empower them to conduct efficient and effective testing throughout the entire testing lifecycle.
Insomnia’s robust features, including comprehensive testing functionalities, flexible environment management, and advanced validation capabilities, enable testers to tackle a wide range of testing scenarios with ease and confidence. The platform’s seamless integration with development workflows, collaborative workspaces, and extensibility through plugins further enhance its utility, allowing testers to seamlessly integrate API testing into their existing processes and workflows.
By leveraging Insomnia’s capabilities, testers can streamline their testing efforts, identify and address issues proactively, and deliver high-quality software products that meet the expectations of end-users.
REFERENCE
https://docs.insomnia.rest/insomnia/get-started


