
What is a Databricks cluster?
A Databricks cluster is a computational resource in the Databricks Unified Analytics Platform designed to process data and run computations efficiently. It provides a set of virtual machines (VMs) that work together to execute distributed data processing tasks. Databricks clusters are particularly optimized for Apache Spark, a powerful open-source data processing engine.
Cluster Components: Worker Nodes and Driver Nodes
Driver Node: The driver node is responsible for preserving the state information of all notebooks linked to the cluster.The driver node understands and executes commands from your notebook or library on the cluster. It also runs the Apache Spark master, which coordinates with the Spark executors.
Worker Node: When the driver node distributes the workload, the processing occurs on worker nodes.For executing a Spark job, a minimum of one worker node is required. You can execute non-Spark commands on the driver node if there are no workers within a cluster but Spark commands will fail.

Types of Clusters in Databricks
- All purpose clusters: All purpose clusters are created manually via GUI, CLI or API.They are persistent means they can be terminated and restarted at any point of time.They can be shared among multiple users but they are more costly to operate compared to job clusters.
- Job clusters: Job clusters are generated when a job begins its execution, and the job has been configured to utilize the cluster.They are suitable for automated workloads like running ETL pipelines or ML workflows.A job cluster gets terminated upon completion of the job and cannot be restarted.

How Do I Create a New Cluster in Azure Databricks?
Step 1: Click on compute icon in your workspace sidebar.
Step 2: Click the “create compute” button where you will select the required configurations.

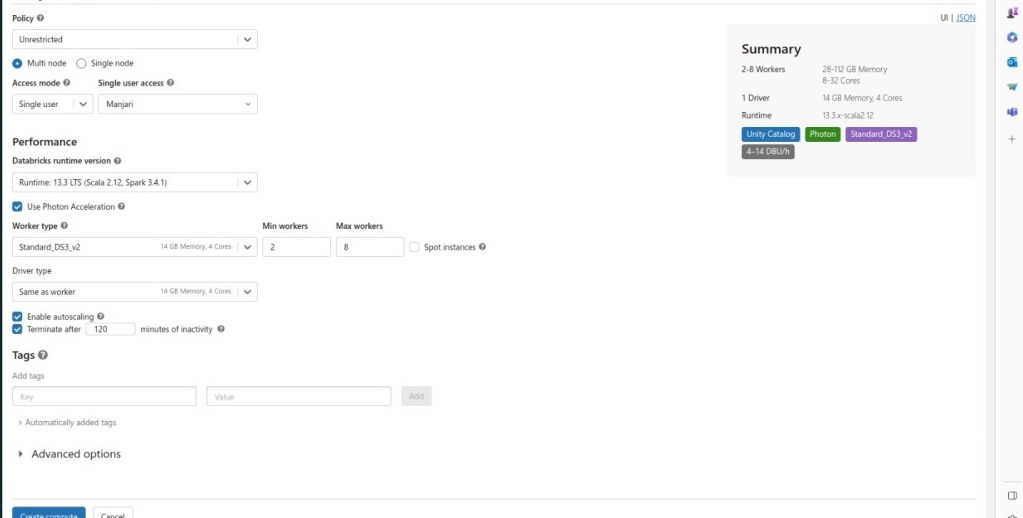
Cluster Configuration Management in Azure Databricks
- Single/MultiNode:
- Multi-node clusters: Multi-node clusters have one driver node and one or more worker nodes. They provide the ability to horizontally scale the cluster depending on your workload. These are the default types of clusters used for Spark jobs and are suitable for large workloads.
- Single-node clusters: Single-node clusters have only one node, which is the driver node and has no worker nodes. When you run a job, the driver node acts as both the driver and worker node. As there are no worker nodes, single-node clusters are not horizontally scalable.
- Access Mode:
- Single User- Single-user access mode permits only one user to access the cluster and supports four languages: Python, SQL, Scala, and R.
- Shared – Shared access allows multiple users to share access. It is only available in premium workspaces and supports Python and SQL.
- No isolation shared – Shared access with no isolation allows more than one user to access and collaborate. It is available in both standard and premium workspaces, supporting four languages: Python, SQL, Scala, and R. The key distinction between shared access and no isolation is that it does not provide process isolation.
- Auto Termination: Auto Termination is a useful feature that helps avoid unnecessary costs on idle clusters. It automatically terminates the cluster after X minutes of inactivity, with the default value set to 120 minutes. The auto-termination range is from 10 to 1000 minutes.
- Databricks Runtime: Databricks Runtime is an integrated and optimized runtime environment provided by Databricks. It includes features like Delta Lake, pre-installed Java, Scala, Python, and R libraries, as well as GPU support for enhanced computing capabilities.”
- Databricks Runtime Versioning: Databricks releases runtime versions regularly, encompassing Long-Term Support (LTS), feature, and major versions. For more information, visit https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/databricks/release-notes/runtime/databricks-runtime-ver
Databricks Auto Scaling: How Does it Affect Cluster Size?
Autoscaling in Databricks is a dynamic process where the platform adjusts the number of workers based on the varying demands of your job. This feature is particularly beneficial when dealing with tasks that have fluctuating computational needs at different stages. Databricks seamlessly adds workers during resource-intensive phases and removes them when no longer necessary.
The key advantage of autoscaling lies in its ability to optimize cluster utilization without requiring manual provisioning to match specific workloads. This is especially useful for tasks with changing requirements over time, such as exploring a dataset throughout the day.
Autoscaling allows Databricks to intelligently determine the optimal workforce for your job. Enabling autoscaling involves specifying the minimum and maximum number of workers for the cluster.Simply navigate to the “Min workers” and “Max workers” fields next to the Worker type dropdown to set the scaling range.
If you choose not to enable autoscaling, enter a fixed number of workers in the “Workers” field next to the Worker type dropdown.
Conclusion
Databricks clusters offer a versatile and scalable solution for efficient data processing. Whether utilizing shared access or leveraging Auto Scaling, these clusters provide the flexibility needed to meet diverse computing needs. With Databricks, organizations can achieve optimal resource utilization and drive innovation in the realm of big data analytics.



1 thought on “Introduction to clusters in Databricks”
Good to have a nice topic points here. Informative + visually representative one.