Introduction
In the rapidly changing landscape of software development, ensuring the quality of applications is more important than ever. Test automation has emerged as a crucial strategy, and JavaScript, the dominant language for web development, is at the forefront of this movement. Its versatility and wide range of testing frameworks make it a top choice for test automation. This guide is designed for beginners who want to harness the power of JavaScript for test automation. We will explore the fundamental concepts, highlight key frameworks, and provide practical examples to help you kickstart your automation journey. Let’s discover how JavaScript can transform your testing processes and improve overall software quality.
Why use JavaScript for Test Automation?
According to the latest Stack Overflow Survey, JavaScript has been the most commonly used programming language for over a decade. Its popularity makes it a top choice for test automation, as many developers are already familiar with it and use it to create and test a wide range of applications.
Ecosystem
JavaScript offers a diverse range of tools and libraries specifically designed to address various requirements in test automation. Some widely used options include:
- Nightwatch.js: A user-friendly, all-in-one testing solution for end-to-end and functional testing, with built-in support for Selenium WebDriver.
- Mocha: A versatile framework compatible with various assertion libraries.
- Cypress: A cutting-edge solution tailored for seamless end-to-end testing.
- Selenium (via WebDriver): Excellent for browser automation and functional testing.
This vibrant ecosystem equips developers with everything they need, whether they’re writing straightforward unit tests or automating intricate UI workflows.
Getting Started with JavaScript for Test Automation
Setting Up Nightwatch.js for Test Automation
1. Prerequisite
Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager) are required to run Nightwatch.js.
Download and install it from Node.js official website.
Verify the installation:

2. Create a Project Directory
Create a folder for your project:

3. Initialize a Node.js Project
Set up a package.json file for your project by running:
npm init -y4. Install Nightwatch
Install Nightwatch.js as a development dependency:
npm install --save-dev nightwatch
5. Set Up Nightwatch Configuration
Run the configuration to set up Nightwatch:
npx nightwatch initIt will generate a nightwatch.conf.js file and set up tests in your project directory.
6. Install a Browser Driver
Nightwatch requires a browser driver to run tests.
For Chrome:npm install chromedriver --save-dev
7. Write your First Test
Inside the tests folder create a test file, e.g., loginPageTest.js:
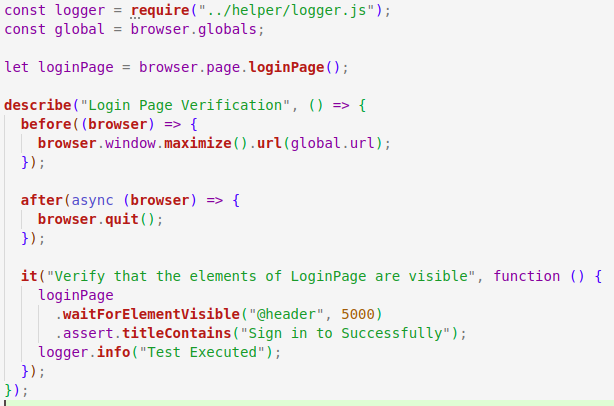
Run your tests using the Nightwatch CLI:
npx nightwatch file pathNow you are all set to start the nightwatch with javascript.
Best Practices for Test Automation
Maintainability:
- Keep tests simple, focused, and reusable.
- Use clear, descriptive names for tests to improve understanding.
- Avoid test duplication by reusing common logic and setup steps.
- Craft each test to function independently for better clarity and easier maintenance.
- Address flaky tests to ensure consistency in results.
Documentation:
- Define each test’s purpose and expected behavior explicitly.
- Document environment and setup details for consistent test replication.
- Add comments to explain complex test logic.
- Use automated reports to track test outcomes and highlight issues, improving visibility for the team.
Integrating with CI/CD
Continuous Integration (CI) streamlines testing by triggering automated runs with each code update. Integrating Nightwatch.js with CI/CD tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions ensures that tests are triggered on each code change, providing instant feedback. This automation helps catch bugs early, reduces manual testing, and maintains high-quality code throughout development, leading to faster, more reliable releases.
Setting up CI/CD to integrate Nightwatch.js
1. Install Dependencies
First, install Nightwatch and other required dependencies, such as chromedriver (for running tests in Chrome):npm install --save-dev nightwatch chromedriver
2. Configure Nightwatch for CI
Make sure younightwatch.conf.js(Nightwatch Configuration file) is set up correctly.
3. Integrate with Github Actions
Create a GitHub Action workflows file (.github/workflows/nightwatch.yml) to automate your tests on push events:
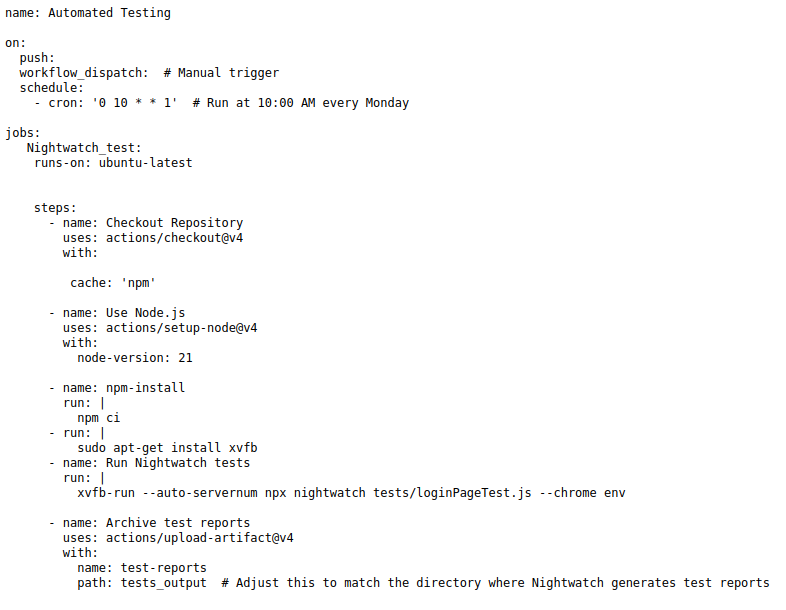
Conclusion:
This guide offers a detailed introduction to starting test automation with JavaScript. By mastering the fundamentals, exploring popular frameworks, and following best practices, you can create reliable and efficient tests to ensure software quality. JavaScript develops to streamline their workflows and deliver robust applications.
Reference:
https://survey.stackoverflow.co/2023/#technology
https://www.lambdatest.com/learning-hub/javascript-automation-testing


