1. Setting up Playwright with C#
- Prerequisites:
– .NET 6 or later
– Visual Studio, Visual Code or any code editor
- Setup source code:
dotnet new console -n PlaywrightCsharpDemo
cd PlaywrightCsharpDemo
- Install Playwright for C#:
dotnet tool install –global Microsoft.Playwright.CLI
dotnet add package Microsoft.Playwright
playwright install
- Install NUnit packages:
dotnet add package Microsoft.NET.Test.Sdk
dotnet add package NUnit
dotnet add package Microsoft.Playwright.NUnit
dotnet add package NUnit3TestAdapter
2. Create test case:
Inheriting from PageTest is essential when building test classes that utilize the Playwright framework with NUnit. The PageTest class provides a pre-configured environment, giving direct access to the Page object—an instance of a browser page—without needing to manually initialize it. This drastically simplifies browser automation code and ensures consistency across all test executions.
With PageTest, you gain:
- Automatic browser context and page setup for each test
- Convenient access to Playwright’s API through
Page - Simplified cleanup and teardown after each test run
- Better integration with NUnit’s test lifecycle
By inheriting PageTest, your test class becomes cleaner, more maintainable, and less error-prone. It’s like getting a fully prepared workspace each time a test runs—perfect for scenarios involving browser navigation, form interactions, and UI validations.

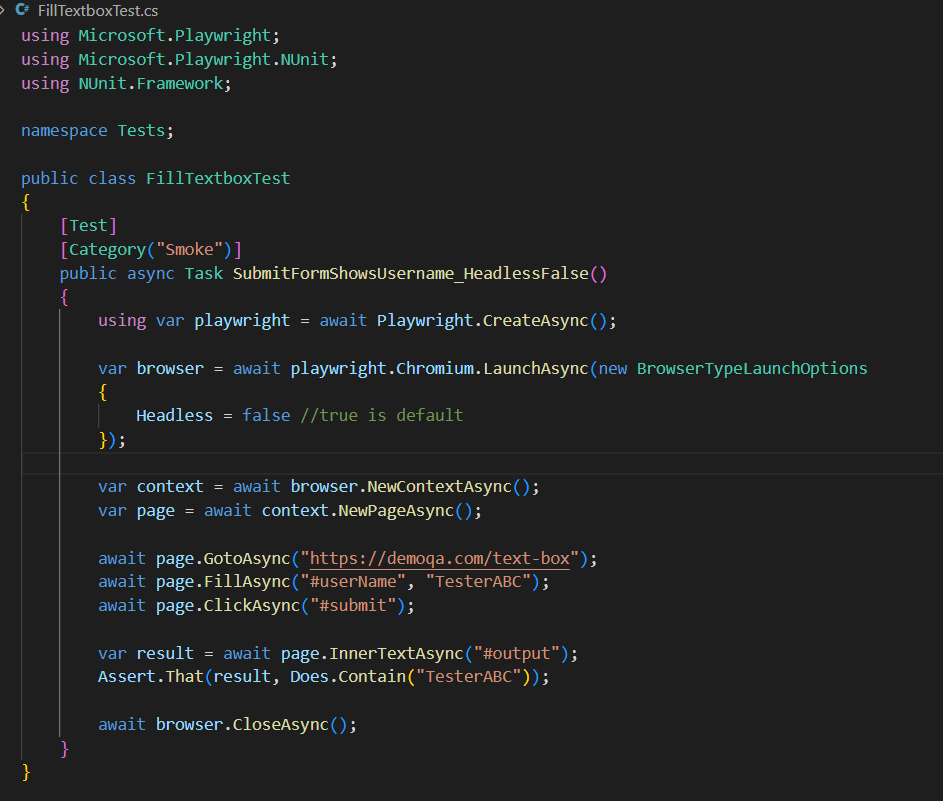
PageTest is great for quick setup—but it limits certain configurations like browser lifecycle, sharing across tests, or advanced launch options.
By writing custom test classes, you gain full control over how and when the browser runs. In the example above, setting Headless = false makes the UI visible, which is useful for debugging or demo purposes.
3. Run test cases:
Execute all test cases:
dotnet test
Execute with specific Test case name
dotnet test –filter “Name= SubmitFormShowsUsername”
Use Class name + Test case name
dotnet test –filter “FullyQualifiedName= Tests. FillTextboxTest. SubmitFormShowsUsername”
Use Category
dotnet test –filter “Category=Smoke”
4. Basic Element Actions
|
Method |
Description |
|
ClickAsync() |
Clicks on the element |
|
FillAsync(selector, text) |
Clears and fills input with the given text |
|
TypeAsync(selector, text) |
Types text into an input (character by character) |
|
PressAsync(key) |
Presses a keyboard key (e.g. Enter, Tab) |
|
GetTextContentAsync() |
Gets all text content of the element |
|
InnerTextAsync() |
Gets only visible text content (like innerText) |
|
InnerHTMLAsync() |
Gets the HTML content inside the element |
|
GetAttributeAsync(name) |
Gets the value of a specified attribute |
|
SetInputFilesAsync(filePath) |
Uploads a file (for <input type=”file”>) |
|
CheckAsync() |
Checks a checkbox or radio button |
|
UncheckAsync() |
Unchecks a checkbox |
|
IsCheckedAsync() |
Checks if a checkbox is selected |
|
IsVisibleAsync() |
Returns true if the element is visible |
|
IsEnabledAsync() |
Returns true if the element is enabled |
|
IsEditableAsync() |
Returns true if the input can be edited |
|
HoverAsync() |
Moves the mouse over the element |
|
FocusAsync() |
Brings focus to the element |
|
ScrollIntoViewIfNeededAsync() |
Scrolls the element into view if it’s outside the viewport |
5. Waiting / Conditions
|
Method |
Description |
|
WaitForSelectorAsync(selector) |
Waits until the element matching selector appears in the DOM |
|
WaitForURLAsync(urlOrRegex) |
Waits until the page URL matches the given value |
|
WaitForLoadStateAsync(state) |
Waits for page load states: load, domcontentloaded, or networkidle |
|
WaitForTimeoutAsync(ms) |
Waits for the specified milliseconds |
|
EvaluateAsync() |
Executes JavaScript code in the page context |
6. Navigation
|
Method |
Description |
|
GotoAsync(url) |
Navigates to the given URL |
|
ReloadAsync() |
Reloads the current page |
|
GoBackAsync() |
Navigates to the previous page |
|
GoForwardAsync() |
Goes forward to the next page in the browser history |


