
Introduction to Snowflake Cortex
Snowflake Cortex is an integrated platform within the Snowflake Data Cloud that empowers organizations to deploy and manage AI and machine learning models directly within their data environment. This platform enables businesses to leverage their data for predictive insights, automation, and enhanced decision-making processes. By providing seamless access to advanced analytics tools, Snowflake Cortex ensures that organizations can fully utilize their data’s potential. As a result, companies can make more informed decisions, stay competitive, and drive innovation across their operations.
Role of AI/ML in enhancing modern analytics.
AI and machine learning (ML) significantly enhance modern analytics by automating and accelerating data analysis. These technologies enable businesses to uncover deeper insights from large datasets, revealing patterns and predicting trends with greater accuracy. By transforming traditional analytics into predictive and prescriptive insights, AI/ML helps organizations anticipate future outcomes and refine their strategies. Consequently, AI/ML not only increases the precision and efficiency of analytics but also drives innovation and provides a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving data landscape.
Key Features of Snowflake Cortex
Seamless Integration with Snowflake
Snowflake Cortex ensures seamless integration with the Snowflake Data Cloud by allowing users to deploy and manage machine learning models directly within the Snowflake environment. This integration streamlines workflows, eliminating the need to transfer data between separate systems and minimizing latency, as all data processing occurs within a unified platform.
In this setup, the integration allows data scientists to perform data preparation, model training, and predictions all within the Snowflake environment, ensuring a streamlined and efficient process.
Prepare Data in Snowflake:
First, ensure that your data is accessible in Snowflake. You can create tables and load data using SQL commands. For example:

Train a Machine Learning Model:
With Snowflake’s support for Python and libraries such as scikit-learn, you can train machine learning models directly within Snowflake. Here is a basic example using Snowpark to handle data and train a model:
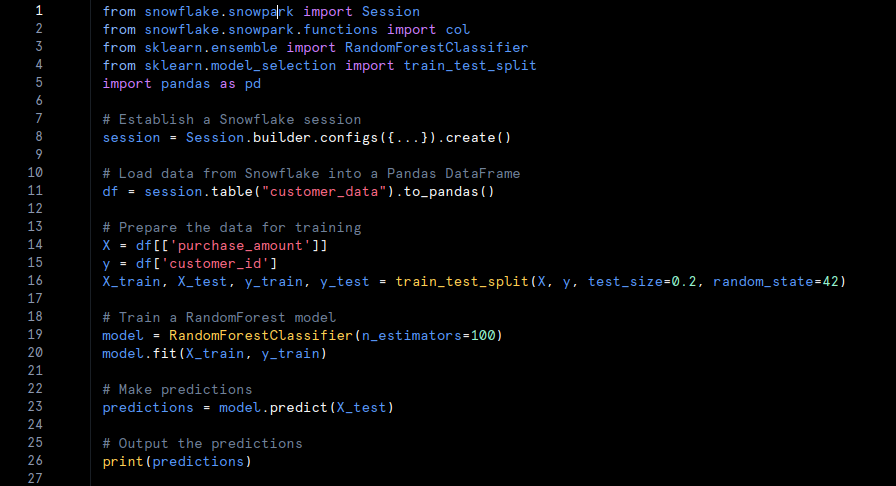
Deploy and Utilize the Model:
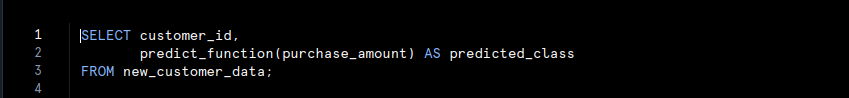
After training the model, you can apply it to new data using Snowflake’s SQL functions. For instance:
Support for AI/ML Models
Snowflake Cortex offers comprehensive support for integrating and managing AI and machine learning (ML) models directly within the Snowflake Data Cloud.
Key Aspects:
- Model Deployment:
- In-Database Deployment: Deploy machine learning models directly within Snowflake, allowing for efficient, in-database processing and real-time analytics.
- Model Management:
- Lifecycle Management: Manage the model lifecycle with features such as version control, monitoring, and updates to ensure models remain accurate and effective.
- Integration with Machine Learning Libraries:
- Library Support: Utilize popular machine learning libraries such as
scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch within Snowflake for model development and deployment.
- Library Support: Utilize popular machine learning libraries such as
- In-Database Training and Inference:
- Efficient Processing: Perform model training and inference within Snowflake, reducing the need for data transfer and ensuring faster processing times.
- Scalable Infrastructure:
- Cloud Scalability: Leverage Snowflake’s cloud infrastructure to handle the computational needs of machine learning models, enabling efficient processing of large datasets.
example of deploying a machine learning model within Snowflake and using it for real-time predictions:
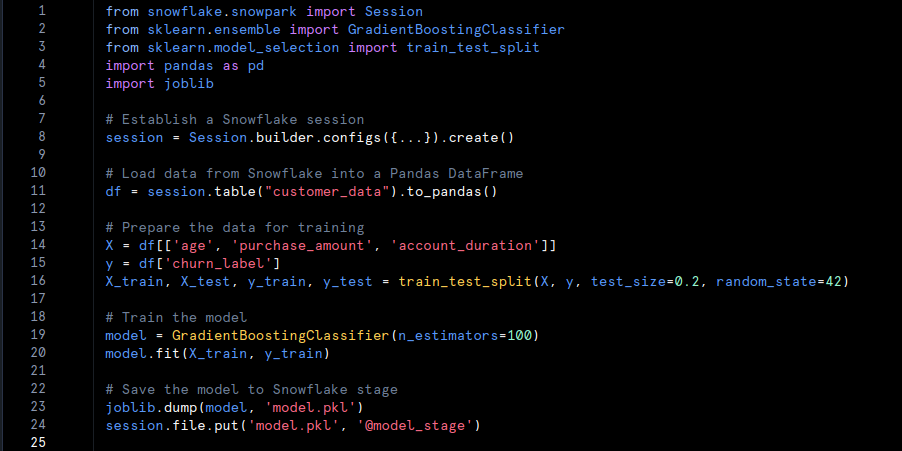
- Train and Save the Model:Train a model using Snowflake’s Python environment.
Use the Model for Predictions:
Define a SQL UDF to apply the trained model to new data:
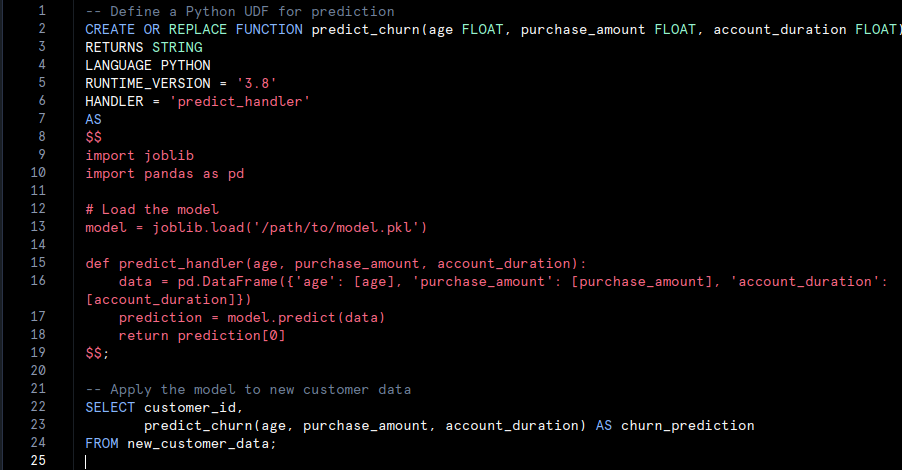
- Model Training: A Gradient Boosting model is trained on customer data and saved to a Snowflake stage for deployment.
- Real-Time Prediction: A Snowflake SQL UDF is created to use the trained model for making predictions on new data.
Custom Model Development
Steps to Build and Train Custom Models
Define Objectives
- Start by clearly defining the problem you want to solve or the task you want the model to perform. This might involve classifying images, predicting user behaviour, or another specific objective.
Collect and Prepare Data
- Split Data: Divide the data into training, validation, and test sets. This separation allows for effective evaluation of the model’s performance.
- Gather Data: Accumulate a diverse and representative dataset that is relevant to your problem.
- Pre-process Data: Clean the dataset to remove noise, address missing values, and normalise or standardise features.
Choose a Framework
- Select a machine learning framework or library that aligns with your needs and expertise. Options include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Hugging Face Transformers.
Design the Model
- Select Architecture: Choose the type of model based on your task. For instance, use convolutional neural networks for image tasks or recurrent neural networks for sequential data.
- Configure Layers: Design the model’s layers and determine the activation functions and other parameters.
- Set Up Loss Functions and Optimizers: Choose appropriate loss functions and optimisation algorithms to guide the model’s learning process.
Train the Model
- Initialise Training: Begin training by feeding the prepared data into the model.
- Monitor Training: Keep track of metrics such as loss and accuracy to ensure the model is learning effectively.
- Adjust Hyper-parameters: Refine hyper-parameters like learning rate, batch size, and number of epochs based on performance observations.
Evaluate the Model
- Test the Model: Assess the model’s performance using the validation and test datasets.
- Analyse Results: Review performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score to gauge how well the model performs.
Fine-Tune the Model
- Refine Hyper-parameters: Make adjustments to hyper-parameters and model architecture to enhance performance.
- Apply Regularisation Techniques: Use methods like dropout or L2 regularisation to prevent over-fitting and improve robustness.
Deploy the Model
- Integrate the Model: Deploy the model into a production environment or application as needed.
- Create APIs: If necessary, provide access to the model via APIs to facilitate its use.
Monitor and Maintain
- Track Performance: Continuously monitor how the model performs in real-world scenarios.
- Update the Model: Periodically retrain or update the model to reflect new data or changes in the environment.
Tips for Optimising Performance
Feature Engine
- Develop and select features that enhance the model’s predictive capabilities. Experiment with different features to determine which are most relevant.
Hyper-parameter Tuning
- Employ techniques such as grid search or random search to find the optimal hyper-parameters for your model. Automated tools like Optuna can also assist in this process.
Cross-Validation
- Implement cross-validation to ensure that the model generalises well across different data subsets, reducing the risk of over-fitting.
Regularization
- Use regularisation methods such as dropout or L1/L2 regularisation to mitigate over-fitting and enhance model generalisation.
Ensemble Methods
- Combine multiple models to improve overall performance. Techniques like bagging, boosting, and stacking can increase prediction accuracy.
Data Augmentation
- Apply data augmentation techniques to artificially expand your training dataset, which can help the model generalise better.
Optimise Computational Resources
- Utilise efficient algorithms and leverage hardware acceleration, such as GPUs or TPUs, to expedite training and inference processes.
Monitor Over-fitting and Under-fitting
- Regularly check for signs of overfitting (good performance on training data but poor performance on test data) or underfitting (poor performance on both training and test data) and adjust your approach as needed.
Keep Abreast of Advances
- Stay updated with the latest developments and research in machine learning to continually refine and improve your model.
Overview of Pre-Trained Models
Pre-trained models are machine learning models that have already been trained on large datasets for specific tasks or a variety of tasks. Instead of building a model from scratch, you can leverage these pre-trained models as a foundation for your applications. By utilizing their embedded knowledge, you can save time and computational resources, especially when handling complex tasks like natural language processing (NLP) or computer vision.
Pre-trained models typically come in two main forms.
Fixed models
- Fixed models which are used as they are without any modifications. These models are ideal when the task at hand closely aligns with the original training data.
Fined-tuned models
- Fine-tuned models, where the pre-trained model is adapted to a new, specific task by further training on a smaller, task-specific dataset. Fine-tuning allows the model to perform better on tasks that differ slightly from its original training objectives.
Key Applications of Pre-Trained Models
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Pre-trained models such as BERT or GPT can be used for text classification tasks, like detecting spam or analyzing sentiment.
- They are also employed for named entity recognition (NER), where the model identifies and categorizes entities such as names, dates, and locations within text.
- Additionally, models like OpenNMT are used for machine translation, converting text from one language to another.
- Moreover, models such as T5 are effective for text summarization, creating concise summaries from longer texts.
Computer Vision
- In computer vision, pre-trained models like ResNet, Inception, and VGG are utilized for image classification, categorizing images into predefined classes.
- Models such as YOLO or Faster R-CNN are commonly used for object detection, identifying and classifying objects within images.
- For tasks requiring image segmentation, models like U-Net or Mask R-CNN segment images into different regions or objects.
- Furthermore, models like FaceNet are widely used in facial recognition, recognizing and verifying identities based on facial features.
Speech Recognition
- Automatic speech recognition (ASR) models like DeepSpeech or Wav2Vec convert spoken language into text, facilitating transcription and voice command applications.
- In speech synthesis, models such as Tacotron generate human-like speech from text, widely used in virtual assistants and text-to-speech applications.
Generative Models
- In text generation, models like GPT-3 can produce coherent and contextually relevant text, which is useful for chatbots, content creation, and other applications.
- Image generation models, such as those using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) like StyleGAN, can create realistic images from random noise or specific inputs.
- Additionally, models like OpenAI’s MuseNet can compose music, while others generate art or design elements, demonstrating their utility in music and art generation.
Transfer Learning
- Pre-trained models are often employed for domain adaptation, where they are fine-tuned to perform well on tasks from a different domain or with a different dataset. This versatility makes them applicable across a wide range of scenarios.
Workflow Integration
Integrating pre-trained models into existing workflows requires ensuring compatibility with ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and BI (Business Intelligence) tools. These tools are essential for managing data pipelines and generating insights, and thus, they must seamlessly work with machine learning models to maintain smooth operations.
Compatibility with ETL Tools
Data Preparation
- ETL tools such as Talend, Informatica, and Apache Nifi are used to extract data from various sources, transform it into the desired format, and load it into a data warehouse or data lake. Pre-trained models can be integrated into this process to enhance data processing. For instance, a pre-trained NLP model could categorize text data during the transformation phase.
Model Integration
- ETL tools often support integration with machine learning models via APIs or custom scripts. By deploying a pre-trained model as a service, you can invoke it from the ETL pipeline to perform tasks like classification, prediction, or anomaly detection on incoming data.
Automation
- Incorporating pre-trained models into ETL workflows enables the automation of tasks such as real-time data classification or sentiment analysis. This automation ensures that insights are generated and actions are taken without manual intervention, thus improving operational efficiency.
Compatibility with BI Tools
Data Visualisation
- BI tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker are designed to visualize data and generate reports. By integrating pre-trained models, these tools can be enhanced to provide predictive analytics. For example, a BI dashboard could include forecasts generated by a pre-trained time series model.
Embedding Predictions
- Many BI tools support embedding machine learning predictions directly into reports or dashboards. Integrating a pre-trained model allows for real-time predictions to be displayed alongside historical data, giving users a more comprehensive view of trends and patterns.
Custom Analytics
- Pre-trained models can be utilized to create custom analytics functions within BI tools. For example, a sentiment analysis model could analyze customer feedback data and present the results in a BI dashboard, enabling decision-makers to act on customer sentiment insights.
Ensuring Seamless Integration
To ensure a smooth integration of pre-trained models with ETL and BI tools, it is crucial to consider several factors:
API Compatibility
- Ensure that the pre-trained model is accessible through APIs that are compatible with the ETL or BI tool in use. RESTful APIs are commonly supported, making integration more straightforward.
Performance Considerations
- Evaluate the performance impact of running pre-trained models within your data pipelines. It is essential that the model’s inference time aligns with the needs of your ETL or BI processes to avoid bottlenecks.
Scalability
- Consider the scalability of the pre-trained model when integrated into ETL workflows. The model should be capable of handling large volumes of data without significant performance degradation.
Security and Compliance
- Ensure that the integration complies with data security and privacy regulations, especially if the pre-trained model processes sensitive information.
Industry Use Cases
Pre-trained models are transforming various industries by providing powerful, real-world applications. These models drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making across sectors.
1. Healthcare
- Medical Imaging: Pre-trained models are extensively used in medical imaging to detect and diagnose diseases such as cancer. For instance, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), trained on large datasets, identify tumors in MRI or CT scans with high accuracy. This application assists radiologists in making early diagnoses.
- Drug Discovery: Pharmaceutical companies employ pre-trained models to predict interactions between drugs and biological targets. By using models like DeepChem, potential drug candidates are screened, accelerating the discovery process and significantly reducing costs.
- Personalized Medicine: In personalized medicine, machine learning models analyze patient data to create tailored treatment plans. By examining genetic information and medical histories, pre-trained models predict how patients will respond to specific treatments, leading to more effective care.
2. Finance
- Fraud Detection: Pre-trained models are essential in detecting fraudulent transactions within the financial sector. Banks and financial institutions use models like autoencoders or random forests, trained on historical transaction data, to identify unusual patterns and flag potential fraud in real time.
- Algorithmic Trading: In algorithmic trading, pre-trained models predict stock prices and market trends. Traders use models like LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) networks, which have been trained on historical market data, to make informed decisions by forecasting short-term market movements.
- Credit Scoring: Financial institutions rely on pre-trained models to assess credit risk. These models analyze various factors, such as income, credit history, and spending patterns, to determine a borrower’s creditworthiness, thus enabling more accurate lending decisions.
3. Retail
- Customer Personalization: Retailers use pre-trained models to deliver personalized customer experiences. By analyzing purchase history and browsing behavior, models recommend products tailored to individual customers, thereby increasing sales and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Inventory Management: In retail, machine learning models optimize inventory levels by predicting product demand. By considering historical sales data and external factors like seasonality, these models ensure that stores maintain appropriate stock levels, reducing waste and preventing stockouts.
- Sentiment Analysis: Retailers also employ sentiment analysis models to monitor customer feedback across social media and review platforms. This capability allows them to gauge customer satisfaction and adjust their strategies accordingly.
4. Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance: In manufacturing, pre-trained models predict equipment failures before they occur. By analyzing sensor data from machines, these models detect patterns that indicate potential breakdowns, allowing for timely maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Quality Control: Machine learning models automate quality control processes in manufacturing. For example, computer vision models inspect products on production lines, detecting defects that might be missed by human inspectors. This ensures high-quality output and reduces errors.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Manufacturers use pre-trained models to optimize their supply chains. By analyzing data from various sources, these models predict disruptions, optimize routes, and manage inventory levels, leading to more efficient operations.
5. Transportation
- Autonomous Vehicles: Pre-trained models are crucial in developing autonomous vehicles. Trained on vast datasets of driving scenarios, these models make real-time decisions, such as recognizing traffic signs, detecting pedestrians, and navigating roads safely.
- Route Optimization: Transportation companies use machine learning models to optimize delivery routes. By analyzing traffic patterns, weather conditions, and schedules, these models select the most efficient routes, thereby reducing fuel consumption and delivery times.
- Fleet Management Predictive Maintenance: Similar to manufacturing, transportation companies employ predictive maintenance models to monitor fleet health. By analyzing vehicle data, these models predict when maintenance is required, preventing costly breakdowns.
6. Energy
- Demand Forecasting: Energy companies use pre-trained models to forecast energy demand. By analyzing historical usage data and external factors like weather, these models help balance supply and demand, ensuring reliable energy distribution.
- Renewable Energy Management: In the renewable energy sector, machine learning models optimize the operation of wind turbines and solar panels. For instance, models predict wind speeds and sunlight intensity, helping maximize energy generation and efficiency.
- Smart Grid Management: Pre-trained models are also used to manage smart grids. These models analyze data from various sensors across the grid, detecting anomalies, preventing outages, and optimizing energy distribution in real time.
7. Entertainment
- Content Recommendation: Streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify use pre-trained models to recommend content. By analyzing viewing and listening habits, these models suggest movies, shows, or music that users are likely to enjoy, enhancing user engagement.
- Personalized Advertising: In the entertainment industry, pre-trained models drive personalized advertising. By analyzing user data, these models help advertisers target specific audiences with relevant ads, thereby increasing engagement and ad effectiveness.
- Content Creation: Machine learning models are also used to create content. For example, generative models can compose music, write scripts, or generate visual art, enabling new forms of creativity in the entertainment sector.
Scalability and Security
Managing large datasets while ensuring compliance and security requires careful planning and implementation of best practices. Both scalability and security are critical to maintaining efficient and secure operations as data volumes grow.
Managing Large Datasets
Scalable Infrastructure
- As data grows, the infrastructure must scale to accommodate increasing demands. Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide scalable computing resources that automatically adjust based on workload. This elasticity allows organizations to maintain performance even as data volumes rise.
- Additionally, distributed computing frameworks such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark are widely used to process large datasets in parallel. These frameworks distribute data processing tasks across multiple nodes, enhancing efficiency and enabling the management of massive datasets.
Efficient Data Storage
- Storing large datasets requires solutions that offer both capacity and speed. Cloud storage services, including Amazon S3 and Azure Blob Storage, provide scalable storage that grows with data needs. These services ensure data is readily accessible while maintaining performance.
- Data lakes and data warehouses serve different purposes but are often used in conjunction. While data lakes store raw, unstructured data, data warehouses are optimized for structured data and analytical queries. Using the right combination of these storage methods can improve data retrieval times and processing efficiency.
Optimized Data Processing
- Efficiently managing large datasets also involves optimizing data processing workflows. Techniques such as data partitioning, indexing, and caching reduce processing time by enabling quicker access to frequently used data.
- Furthermore, data pipelines should support both batch processing and real-time data streaming. Tools like Apache Kafka and Google Dataflow facilitate real-time data processing, ensuring that insights are generated promptly, even with large volumes of data.
Ensuring Compliance and Security
Data Encryption
- Protecting data, particularly sensitive information, is crucial. Data encryption at rest and in transit is necessary to prevent unauthorized access. Services like AWS KMS and Azure Key Vault provide encryption key management, ensuring that data remains secure.
- Implementing end-to-end encryption further strengthens security by safeguarding data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to transfer and storage, thereby minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Access Control
- Securing data access requires robust access control measures. Role-based access control (RBAC) allows organizations to define roles and assign permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access specific data.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, requiring users to verify their identity through multiple factors. This measure protects data even if login credentials are compromised.
Compliance with Regulations
- Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA is essential when managing large datasets. Organizations must implement data handling and privacy policies that adhere to these regulations to avoid penalties and maintain trust.
- Regular audits and assessments are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that practices align with regulatory requirements. Techniques like data anonymization and pseudonymization protect personal data while allowing for its analysis, ensuring compliance with privacy laws.
Monitoring and Incident Response
- Continuous monitoring of data systems is vital for detecting and responding to security incidents. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools like Splunk and IBM QRadar provide real-time monitoring, alerting, and analysis of security events, enabling proactive incident management.
- An incident response plan should be in place to address data breaches or security threats. This plan must include steps for containment, eradication, recovery, and communication, ensuring that responses are swift and effective.
Future of AI/ML with Snowflake
Snowflake is actively shaping the future of AI and machine learning (ML) by integrating advanced capabilities into its data platform. As these technologies evolve, several emerging trends and upcoming features will significantly impact how organizations leverage AI/ML with Snowflake.
Emerging Trends
Integration of AI/ML Workflows
- Snowflake is becoming a central hub for AI/ML workflows due to its seamless integration with various machine learning platforms and tools. This trend reflects the growing demand for end-to-end AI/ML pipelines that allow data scientists to perform everything from data ingestion to model deployment within a single environment.
- Furthermore, the rise of Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) within Snowflake is simplifying model development, enabling users to create, train, and deploy models without needing deep expertise in machine learning. This democratization of AI/ML tools is expanding access to these powerful technologies.
Advanced Data Sharing and Collaboration
- As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven insights, Snowflake’s secure data sharing capabilities are evolving to support collaborative AI/ML efforts across different teams and even across organizations. This shift is fostering a more collaborative approach to AI/ML, where data and models can be shared and reused to accelerate innovation.
- Additionally, the emergence of data marketplaces within Snowflake is facilitating the exchange of AI/ML models and datasets between organizations. This trend is paving the way for new business models and partnerships centered around data and AI-driven insights.
Real-Time Data Processing for AI/ML
- Real-time data processing is becoming crucial for AI/ML applications that require immediate insights, such as predictive maintenance, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations. Snowflake’s advancements in real-time data streaming and processing are enabling AI/ML models to be continuously updated with fresh data, ensuring that predictions and insights remain accurate and timely.
- The integration of streaming data sources within Snowflake is expected to expand, providing organizations with the capability to feed real-time data into their AI/ML models, resulting in more dynamic and responsive applications.
Upcoming Features
Native AI/ML Model Hosting
- One of the most anticipated features on Snowflake’s roadmap is the ability to host and deploy machine learning models natively within the platform. This capability will eliminate the need to export data to external platforms for model training and inference, reducing latency and enhancing security.
- Native model hosting will also enable tighter integration with Snowflake’s data governance and security features, ensuring that models comply with organizational policies and regulatory requirements.
Enhanced AI/ML Tooling with Snowpark
- Snowpark, Snowflake’s developer framework, is set to introduce more advanced AI/ML tooling. This enhancement will allow developers to write custom code in languages like Python, Scala, and Java to manipulate data directly within Snowflake. The result will be more complex data transformations and model training workflows that are tightly integrated with the platform.
- With the expansion of Snowpark, data scientists and engineers can expect stronger support for AI/ML libraries and frameworks, further embedding their machine learning workflows within Snowflake’s ecosystem.
AI-Powered Data Governance
- As data governance becomes increasingly critical, Snowflake is exploring the use of AI to enhance data governance and compliance features. AI-driven tools will be used to automatically classify sensitive data, detect anomalies, and enforce data access policies based on usage patterns.
- This AI-powered governance will improve data security and simplify compliance with regulations by automating many tasks traditionally handled manually, such as auditing and reporting.
Increased Support for Pre-Trained Models and Transfer Learning
- Snowflake is expected to expand its support for pre-trained models and transfer learning. This feature will allow users to leverage existing models and apply them to their specific data with minimal customization, speeding up the deployment of AI/ML applications.
- This capability will be particularly beneficial for organizations that want to implement AI/ML solutions quickly by using models that have already been validated in similar contexts.
Conclusion
In summary, Snowflake is transforming the landscape of AI and machine learning (ML) with its innovative features and integrations. Here’s a brief overview and actionable insights:
Summary
Key features on the horizon include native model hosting, enhanced tooling with Snowpark, AI-driven data governance, and support for pre-trained models. These updates will streamline model deployment and improve data management.
Integration and Innovation
- Snowflake integrates AI/ML workflows, connecting seamlessly with various tools and enabling end-to-end pipelines. This integration supports AutoML, making model development and deployment more accessible.
Real-Time Processing
- Snowflake advances real-time data processing, crucial for applications needing immediate insights, such as fraud detection and personalized recommendations. This ensures AI/ML models use the most current data.
Upcoming Features
- Key features on the horizon include native model hosting, enhanced tooling with Snowpark, AI-driven data governance, and support for pre-trained models. These updates will streamline model deployment and improve data management.

