1. What is Integration Testing?
Integration Testing is a level of software testing where individual units are combined and tested as a group. The purpose of this level of testing is to expose faults in the interaction between integrated units.
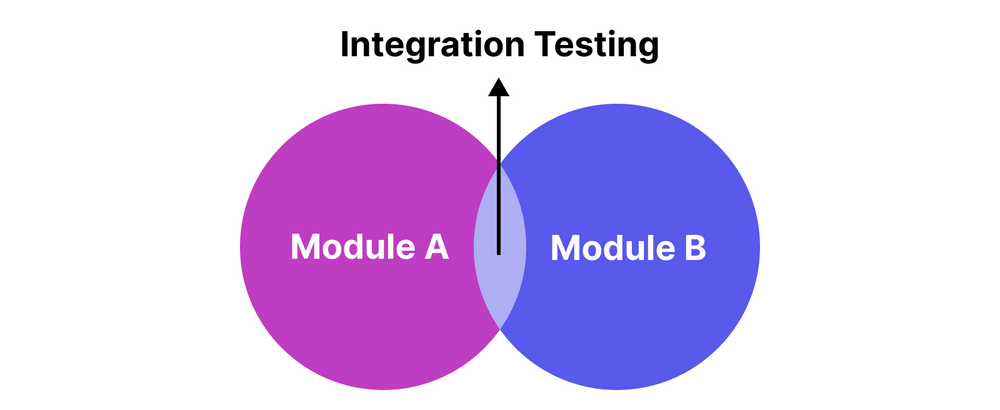
2. When is Integration Testing Performed?
Integration testing is performed after unit testing and before system testing. It takes place in the middle of the testing process, once all the individual units or components of a software system have been unit tested, but before the system as a whole is tested.
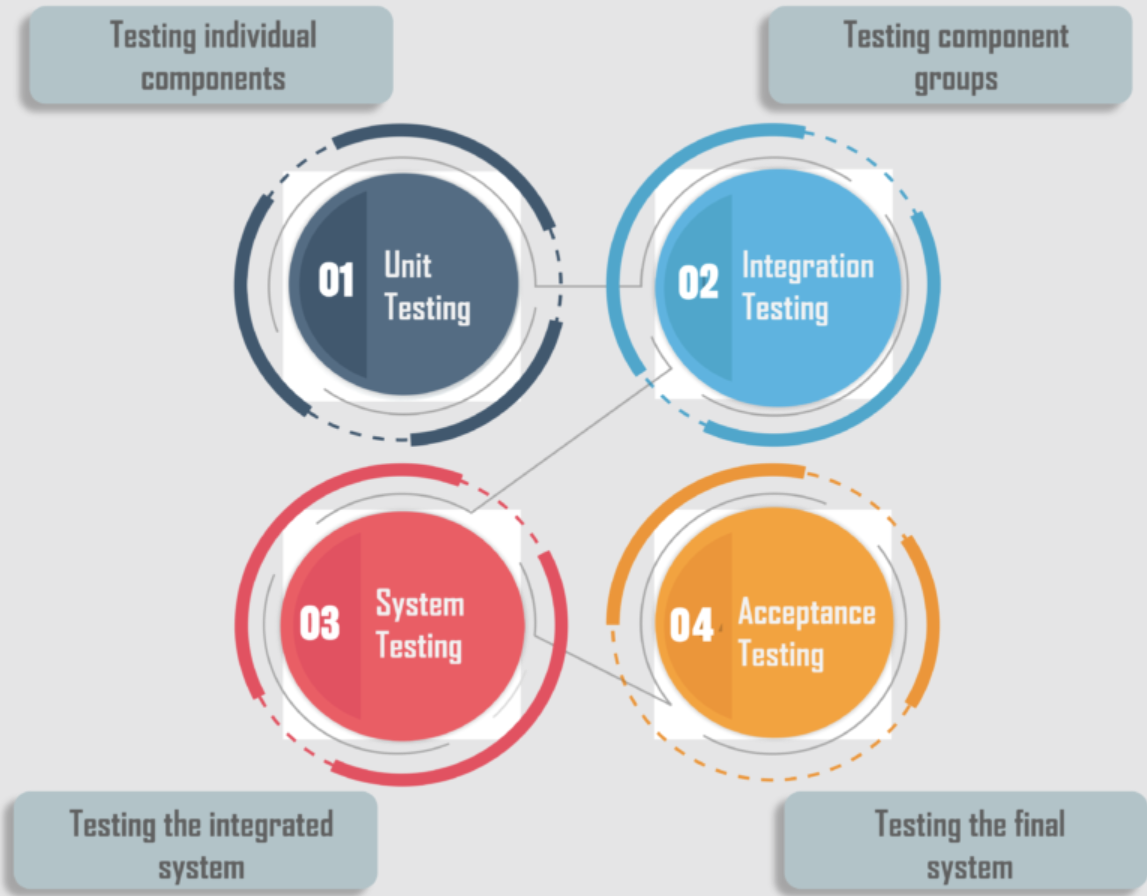
3. Why is Integration Testing Important?
Integration testing is important for several reasons:
- Detecting Interface Issues: It helps in finding issues related to the communication between different modules of a software system.
- Verifying System Functionality: It ensures that the integrated modules work properly when they are grouped.
- Identifying Problems Early: It helps in identifying and addressing problems early in the development cycle, which reduces the cost and effort of fixing them later.
4. How to Perform Integration Testing?
Integration testing can be performed using different approaches:

4.1. Big Bang Approach
In this testing approach, once all the modules are developed and tested individually, they are integrated once and tested together at once. The only advantage of this type of testing is that it is very much suitable for smaller systems.

Advantages:
- It is useful when the system has a small number of modules.
- It is simple to use as there’s no need for stubs or drivers.
Disadvantages:
- It’s hard to isolate errors.
- It’s not suitable for large projects as it can lead to higher defect fixing costs and time.
4.2. Incremental Approach
This approach is performed by connecting two or more modules together that are logically related. Later more modules are added and tested for proper functionality. This is done until all the modules are integrated and tested successfully. It’s further divided into Top-Down Approach, Bottom-Up Approach, and Sandwich Approach.
4.2.1. Top-Down Integration Testing
The top-down approach starts by testing the top-most modules and gradually moving down to the lowest set of modules one-by-one. Testing takes place from top to down following the control flow of the software system. As there is a possibility that the lower level modules might not have been developed while top modules are tested, we use stubs instead of those not ready modules. For simple applications, stubs would simply return the control to their superior modules. For complex applications, they would simulate the full range of responses.

Advantages:
- Early discovery of high-level design and interface issues.
- Stubs are only needed for modules at the lower levels.
Disadvantages:
- The need for stubs can be a disadvantage as they may not perfectly simulate lower-level modules.
- It’s difficult to conduct early tests of the system as a whole.
4.2.2. Bottom-Up Approach
The bottom-up approach starts with testing the lowest units of the application and gradually moving up one-by-one. Here testing takes place from the bottom of the control flow to upwards. Again it’s possible that the higher level modules might not have been developed by the time lower modules are tested. In such cases, we simulate the functionality of missing modules by using drivers. These drivers perform a range of tasks such as invoking module under test, pass test data or receive output data.
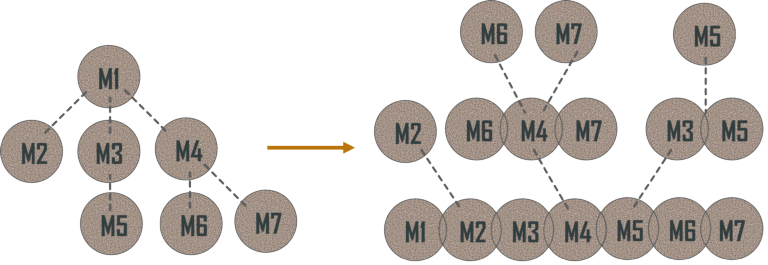
Advantages:
- Early discovery of low-level issues and faults.
- Drivers are only needed for modules at the higher levels.
Disadvantages:
- The need for drivers can be a disadvantage as they may not perfectly simulate higher-level modules.
- It’s difficult to conduct early tests of the system as a whole.
4.2.3. Sandwich (or Hybrid) Approach
To overcome the limitations and to exploit the advantages of top-down and bottom-up approaches, a hybrid approach of integration testing is used. This approach is known as sandwich integration testing or mixed integration testing. Here, the system is viewed as three layers. Main target layer in the middle, another layer above the target layer, and the last layer below the target layer. The top-down approach is used on the layer from the top to the middle layer. The bottom-up approach is used on the layer from the bottom to middle. Big bang approach is used for modules in the middle.

Advantages:
- It’s a more comprehensive method of testing.
- It allows for simultaneous work on both the top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Disadvantages:
- It’s complex due to the need for both stubs and drivers.
- It requires careful planning and design.
5. Challenges of Integration Testing
- Incompatibility Between Software Modules: Each module is designed individually by a software developer. Because of the uniqueness of each module, incompatibility between them can occur and cause errors in a system. To overcome this, ensure that all modules are designed with integration in mind from the start, and use comprehensive integration testing to identify and resolve any compatibility issues.
- Changes in Requirements: During and after module developments, clients may request a change of requirements. Unit tests for such new requirements can be inadequate. To handle this, make sure to include these changes in your integration tests to verify that the new requirements work well with the existing system.
- Interactions with APIs: Software modules often interact with APIs. Integration testing ensures that data transferred via modules to APIs are correct. Regularly update your integration tests to include any new or updated APIs and verify that the data these tools accept is correct.
- Hardware Compatibility Issues: There may be potential problems with hardware compatibility. To mitigate this, include hardware in your integration testing strategy to ensure that your software works correctly on all intended hardware configurations.
- Different Programming Logics: Every software developer has their understanding and programming logic. To ensure smooth functioning, it’s important to have a standard coding style guide that all developers follow. This can help reduce the number of integration issues caused by differing programming logics.
Remember, overcoming these challenges requires a well-planned and executed integration testing strategy. Using the right tools and practices can help ensure that your software is robust, reliable, and ready for release.
6. Conclusion
Integration testing is an indispensable part of software testing that ensures the delivery of a robust, reliable, and high-quality software product to the end-user. It’s a step that developers should not skip, as it ultimately contributes to the success of the software in the real world.
7. Reference
What is Integration Testing? | How to perform integration testing? | Edureka
What is Integration Testing? Definition, Examples, How-to (katalon.com)
What is Integration Testing: Examples, Challenges, and Approaches


