Introduction
A semantic kernel represents the meaning of words or phrases within a specific context, serving as a vital component in natural language processing and machine learning tasks. It provides a mathematical framework for understanding and processing textual data efficiently.
Semantic Kernel as an SDK
Semantic Kernel is an open-source Software Development Kit (SDK) designed to facilitate the integration of existing code with advanced models from platforms like OpenAI, Azure Open AI, and Hugging Face. This extensible SDK empowers developers to construct agents capable of leveraging diverse functionalities to answer queries and automate tasks seamlessly.
Exploring Skills within Semantic Kernel
What are Skills
In the context of Semantic Kernel or analogous systems, a skill denotes a distinct capability or competency enabling a computer program to execute specific tasks effectively. These tasks range from basic arithmetic calculations to intricate functions like natural language understanding and image recognition.
Components of a Skill
Purpose
A skill is crafted with a defined objective within a broader system. For instance, it may aim to extract pertinent information from text, translate between languages, or classify images based on content.
Functionality
Each skill encompasses a set of functionalities, including data processing, pattern recognition, decision-making, or interaction with external systems via APIs.
Input and Output
Typically, a skill receives input in the form of data or instructions and yields meaningful output aligned with its intended purpose. For instance, sentiment analysis might generate sentiments (positive, negative, neutral) from textual input.
Implementation
Skills are realized through algorithms, models, or code that dictate their operations and data processing. This implementation could involve machine learning models, rule-based systems, heuristic algorithms, or a blend of these methods.
Scalability and Adaptability
Ideally, skills should scale and adapt to diverse contexts or domains, accommodating varying data volumes and types. They should also be easily extendable and customizable to address new requirements or use cases.
Performance and Accuracy
Crucially, a skill’s performance and accuracy in task execution are paramount. Skills should be optimized to deliver high performance and accuracy while minimizing computational overheads and processing time.
Types of Skills
The Semantic Kernel framework offers various skills that facilitate different aspects of text processing and analysis. These skills can be broadly categorized into Text Generation, Information Retrieval, and Data Processing. Here, we delve into each type of skill.
Text Generation Skills
Text Generation skills are essential for creating coherent and contextually relevant text. These skills enable applications to generate human-like responses or content, making them useful for a variety of tasks such as storytelling, automated content creation, and chatbots.
Example Code
In this code example, we create a TextGenerator class with a method GenerateText that simulates text generation based on a given prompt. Although this is a simplified placeholder, in a real implementation, you would integrate this with the Semantic Kernel SDK to leverage advanced language models.

In this code, the GenerateText method receives a prompt and a maximum length for the generated text. It returns a placeholder string that includes the prompt. In a practical scenario, this method would interact with a text generation API from the Semantic Kernel SDK.
Information Retrieval Skills
Information Retrieval skills are designed to answer questions by retrieving relevant information from datasets or external APIs. These skills are particularly useful in applications such as search engines, virtual assistants, and knowledge management systems.
Example Code:
In this code, we present a InformationRetriever class with a method RetrieveInformation that answers a query. The provided example is a placeholder, and a real-world application would use Semantic Kernel SDK functionalities to fetch information.
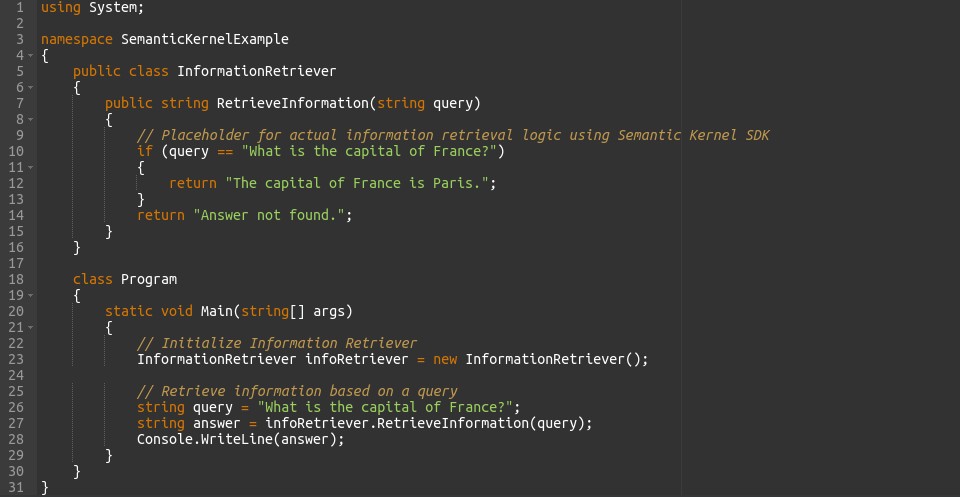
In this code, the RetrieveInformation method takes a query string and returns a predefined answer. In a more sophisticated implementation, this method would interact with a knowledge base or an API to fetch accurate and dynamic responses.
Data Processing Skills
Data Processing skills handle and transform data efficiently. These skills include tasks such as data summarization, aggregation, and manipulation, making them vital for data analysis and preprocessing.
Example Code:
In this example, a DataProcessor class with a method SummarizeData that provides a summary of the given data. This example uses a simple string operation for summarization, but in practice, it would utilize the Semantic Kernel SDK.

In this code, the SummarizeData method takes a string and returns a brief summary. The example simply truncates the text for demonstration purposes. However, a real-world implementation would leverage advanced summarization techniques provided by the Semantic Kernel SDK.
Beginner Guide to Creating Skill
Creating Skills
Creating a new skill in the Semantic Kernel involves several steps, including defining the skill’s purpose, implementing the necessary logic, and integrating it into your application.
Step-by-Step Guide to Defining and Implementing a New Skill:
1. Define the Skill’s Purpose
First and foremost, before writing any code, it’s crucial to clearly define what the skill is supposed to accomplish. For instance, let’s create a skill that performs basic arithmetic operations.
2. Implement the Skill
Next, create a new class for the skill and define methods that fulfil its purpose. In our example, we will develop an ArithmeticSkill class with methods for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
3. Integrate the Skill
Integrate this new skill into your application by instantiating the class and calling its methods as needed.
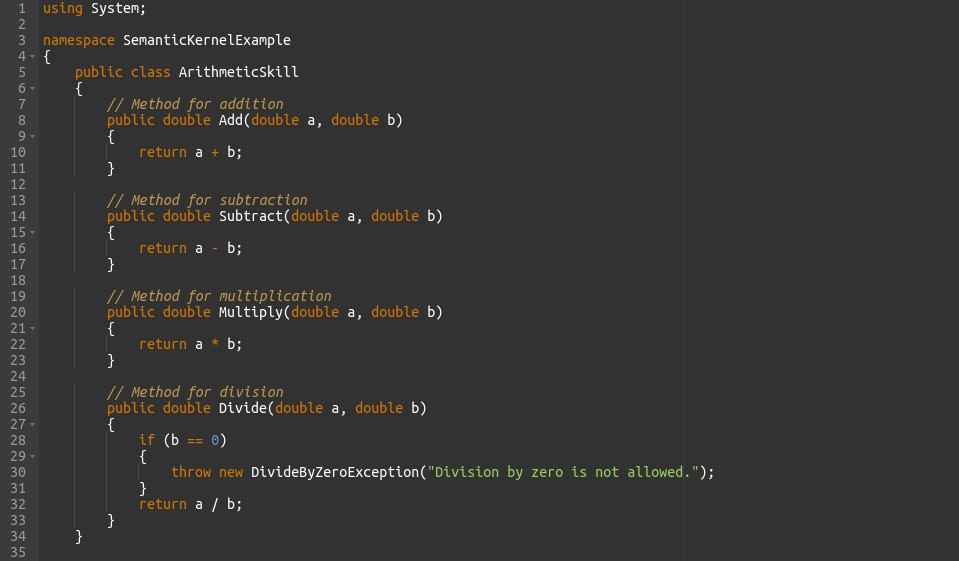

In this code, the ArithmeticSkill class provides methods for basic arithmetic operations like Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division. The Program class demonstrates how to instantiate the skill and use its methods.
Best Practices for Developing Skills
When developing skills within the Semantic Kernel framework, adhering to best practices ensures that your skills are modular, reusable, and well-documented. These practices enhance maintainability and facilitate collaboration among developers.
Modularity
Modularity involves designing skills in a way that they are self-contained and independent. This practice allows you to reuse skills across different projects and makes it easier to maintain and update them.
In the above code example, the ‘ArithmeticSkill’ class encapsulates various arithmetic operations. Each method is independent, and the class can be easily reused in different parts of the application or in other projects.
Documentation
Proper documentation is essential for easier maintenance and collaboration. Documenting your skills helps other developers understand the purpose, functionality, and usage of the skills, leading to more efficient teamwork and smoother project transitions.
Example Code for Documentation in .NET
Adding XML comments to your code is a common practice in .NET for documentation purposes. Here’s how you can document the ArithmeticSkill class:
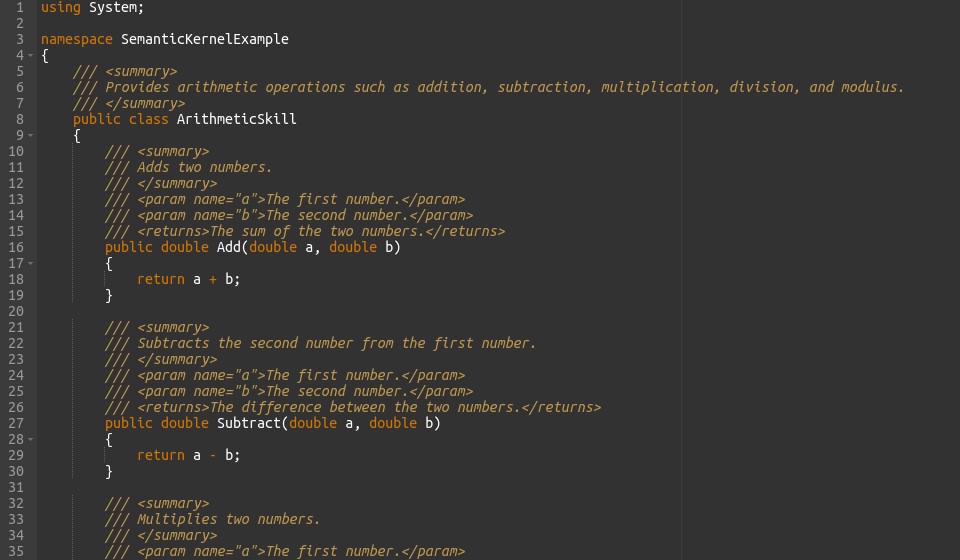
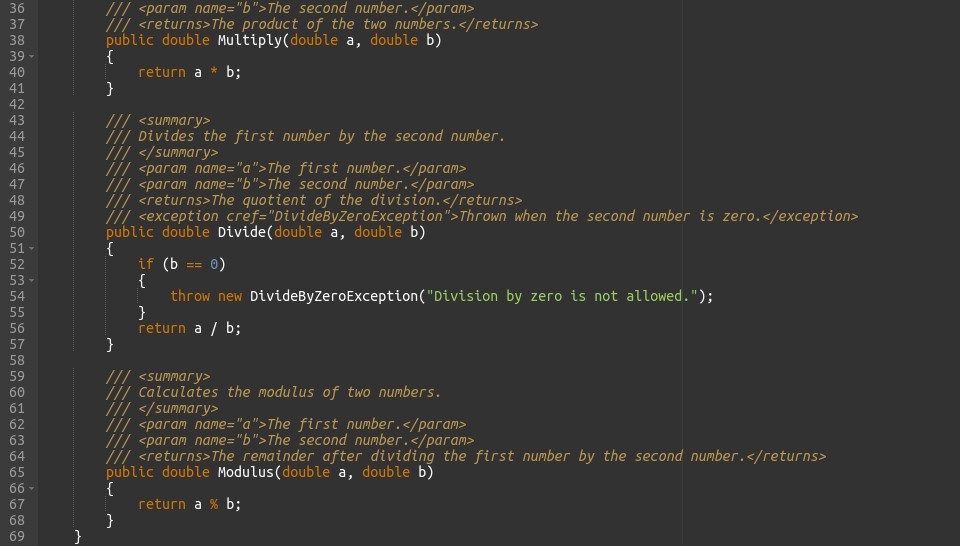
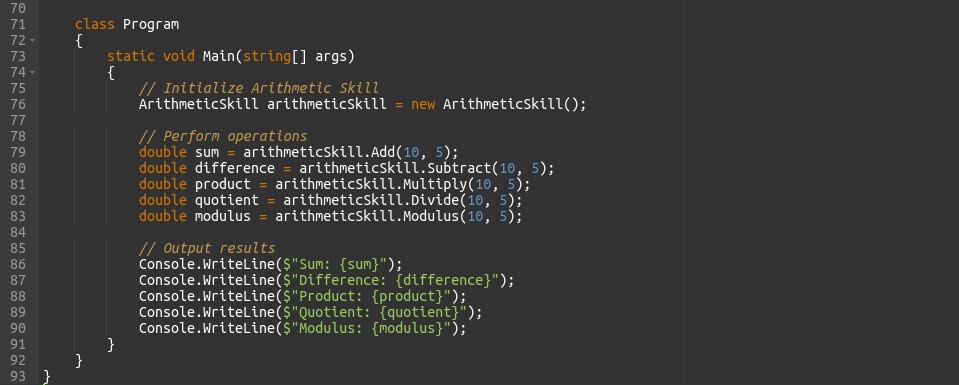
In this example, XML comments are added to each method and class to describe their functionality, parameters, return values, and exceptions. This documentation can be used by tools such as Visual Studio to generate comprehensive documentation and provide IntelliSense support for developers.
Conclusion
In summary, developing skills within the Semantic Kernel framework requires a solid understanding of skill definitions and types. Skills such as Text Generation, Information Retrieval, and Data Processing are essential for various data handling and transformation tasks. By following a structured approach to define and implement new skills, beginners can ensure these skills serve specific purposes and integrate smoothly into applications.
Furthermore, adhering to best practices is crucial. Keeping skills modular and reusable enhances maintainability and flexibility, while proper documentation ensures clarity and facilitates collaboration among developers. By following these guidelines and utilizing detailed code examples, developers can create robust and efficient skills, contributing to more intelligent and effective systems.



