 Introduction
Introduction
Power Apps is a component of Microsoft’s Power Platform that lets users quickly create custom business applications with little or no coding. It provides a development environment for building apps that work on web browsers, smartphones, and tablets, integrating seamlessly with Microsoft services and over 400 data sources.
Role of Power App within the Microsoft Power Platform
The Microsoft Power Platform is a collective term for four key products: Power BI, Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power Virtual Agents. These tools work together to provide a comprehensive solution for data analysis, app creation, process automation, and virtual agent deployment. Each component of the Power Platform plays a specific role, and together, they help organizations streamline operations, drive efficiencies, and make data-driven decisions.
1. Power BI
- Function: Business analytics service that enables users to visualize data, create reports, and gain insights to make informed decisions.
- Integration with Power Apps: Power BI can embed Power Apps to allow users to take action directly from within their reports.
2. Power Apps
- Function: Provides the tools to build custom apps tailored to specific business needs. It enables the creation of both canvas and model-driven apps.
- Role: Central to enabling digital transformation by allowing both technical and non-technical users to create custom solutions that integrate with existing systems and workflows.
- Integration: Works closely with Power Automate for workflow automation and with Dataverse for secure data storage and management.
3. Power Automate
- Function: Workflow automation tool that allows users to create automated workflows between different applications and services.
- Integration with Power Apps: Automate processes triggered by actions within Power Apps, such as approvals, notifications, and data updates.
4. Power Virtual Agents
- Function: Provides tools to create intelligent chatbots without needing extensive coding knowledge.
- Integration with Power Apps: Chatbots can interact with apps created in Power Apps to provide users with a seamless support experience.
Types of Power Apps
It provides a rapid application development environment to build custom apps for your business needs. Within Power Apps, there are three primary types of apps you can create:
1. Canvas Apps
- Design Freedom: Allows for a highly customized user experience where you can design the app’s interface by dragging and dropping elements onto a blank canvas.
- Data Integration: Can connect to a wide variety of data sources, including SharePoint, Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, SQL Server, and many other third-party services through connectors.
- Visual Design: Create apps with a focus on the look and feel, akin to designing a PowerPoint presentation.
- Flexible Layout: Complete control over the app’s layout, making it suitable for custom scenarios and specific business processes.
- Responsive Design: Apps can be designed to be responsive to different screen sizes, which is especially useful for mobile devices.
2. Model-Driven Apps
- Data-Centric Design: Focuses on leveraging the data model and relationships defined within Microsoft Dataverse. The app’s layout is generated based on the data and entities.
- Component Reusability: Uses standard components like forms, views, and dashboards, which are configured rather than designed from scratch.
- Unified Interface: Provides a consistent and responsive user experience across devices automatically.
- Built-in Logic: Includes out-of-the-box features like business process flows, forms, views, charts, and dashboards that can be easily configured.
- Scalability: Well-suited for complex business processes and enterprise applications.
3. Portals
- External Access: Enables the creation of websites that can be accessed by external users, including customers and partners, in addition to internal users.
- Data Interaction: Allows external users to interact with data stored in Microsoft Dataverse through a secure, web-based interface.
- Web-Based Design: Design portals using templates, themes, and configurations in a low-code/no-code environment.
- Authentication: Supports various authentication methods, including Azure AD, LinkedIn, Microsoft Accounts, and more.
- Content Management: Provides features for managing web content, including forms, lists, and custom pages.
Power Apps: Access, Setup, and Initial Steps
Accessing Power Apps
-
Sign Up:
- If you don’t already have a Microsoft account, sign up for one. You can sign up for Power Apps directly by going to the Power Apps Website.
- Click on “Start free” to begin your free trial or sign in if you already have an account.
-
Log In:
- Go to the Power Apps Portal.
- Log in using your Microsoft account credentials.
Basic Setup
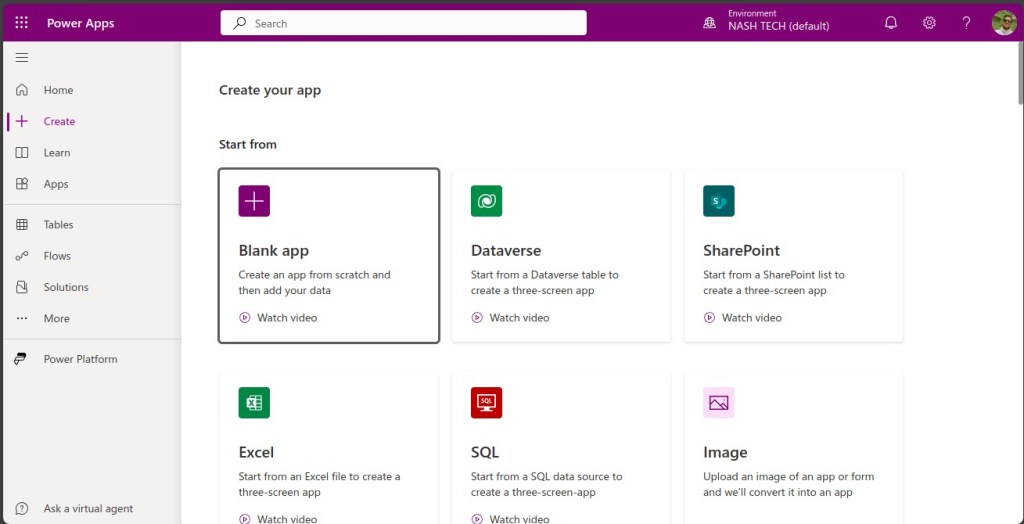
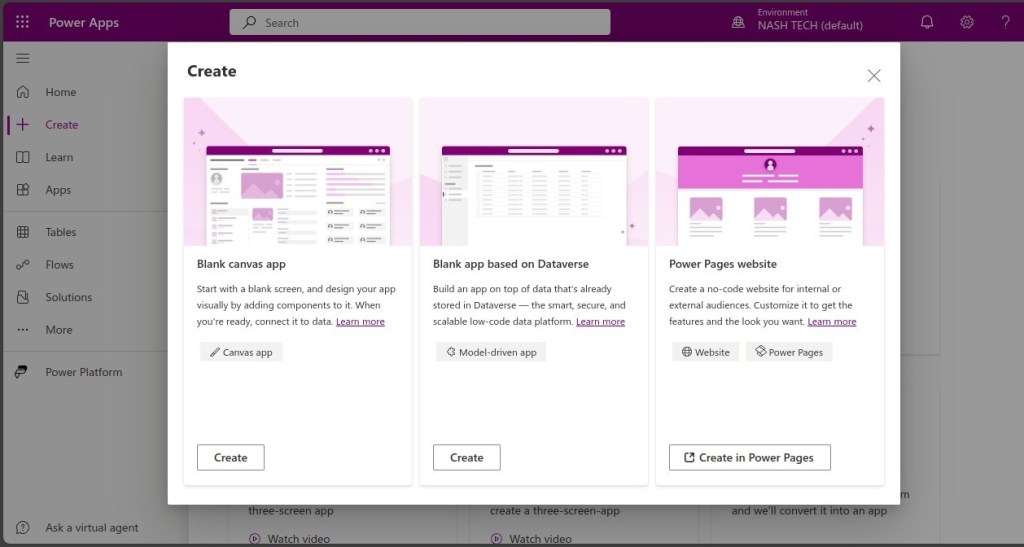
-
Environment Setup
- Once logged in, you’ll be directed to the Power Apps home page.
- Power Apps works within environments. An environment is a space to store, manage, and share your organization’s business data, apps, and flows. You may have multiple environments for different purposes (development, testing, production).
- Select an existing environment or create a new one by clicking on the environment selector in the top-right corner and choosing “+ New environment”.
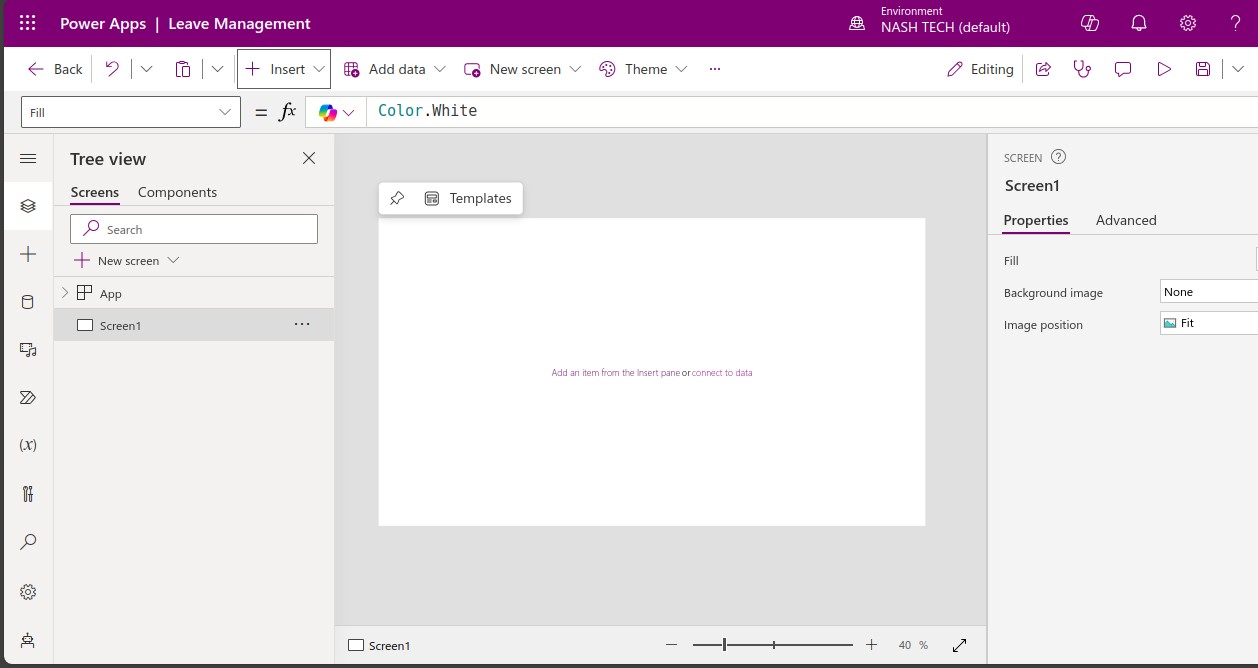
-
Understanding the Interface:
- Home: This is where you can start creating apps, access recent apps, and view learning resources.
- Apps: View and manage all your apps.
- Data: Manage your data sources, entities (tables), and connections.
- Flows: Manage your Power Automate flows.
- Solutions: Group related apps, data, and other resources together.
Initial Steps to Create Your First App
Choose an App Type:
- Power Apps offers two main types of apps: Canvas Apps and Model-Driven Apps.
- Canvas Apps: Provide a drag-and-drop interface where you can design the app layout and connect to various data sources.
- Model-Driven Apps: Focus on leveraging your data model and business processes with less emphasis on custom UI.
How to create our First App
A simple Canvas app in Power Apps:
Step 1: Sign in to Power Apps
- Open Power Apps: Go to Power Apps.
- Log In: Use your Microsoft account to sign in.
Step 2: Create a New Canvas App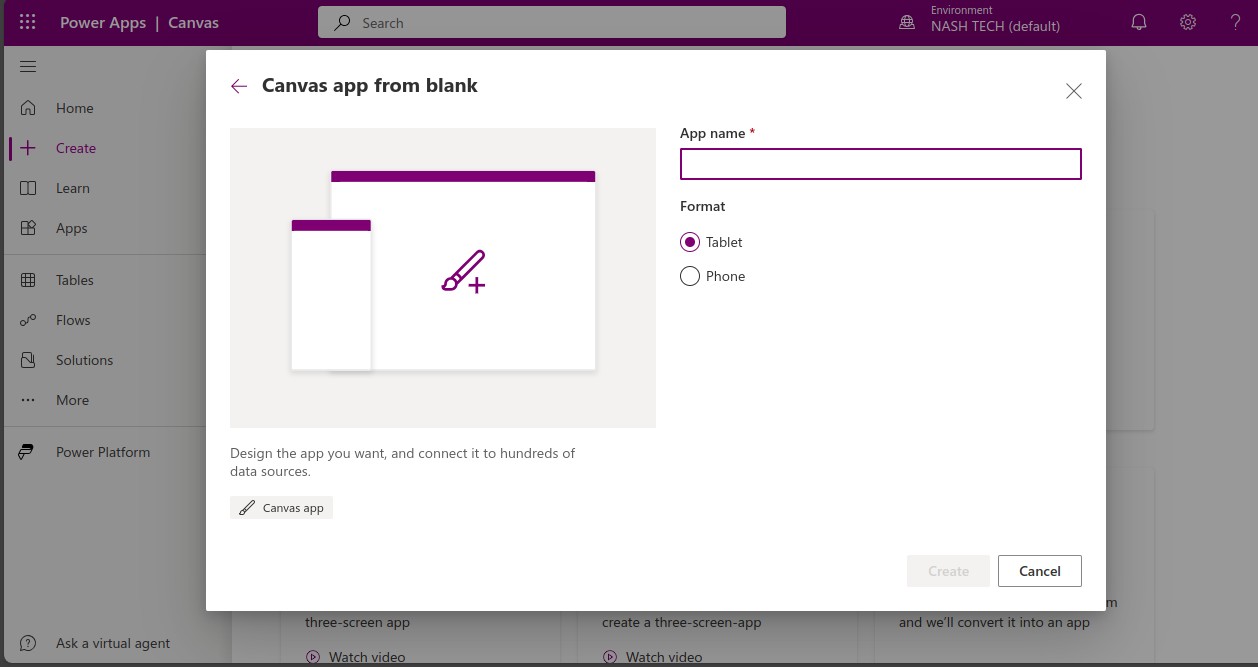
- Start a Blank App: Click “Create” and select “Canvas app from blank.”
- Name and Format: Enter a name and choose either Phone or Tablet format. Click “Create.”
Step 3: Add a Data Source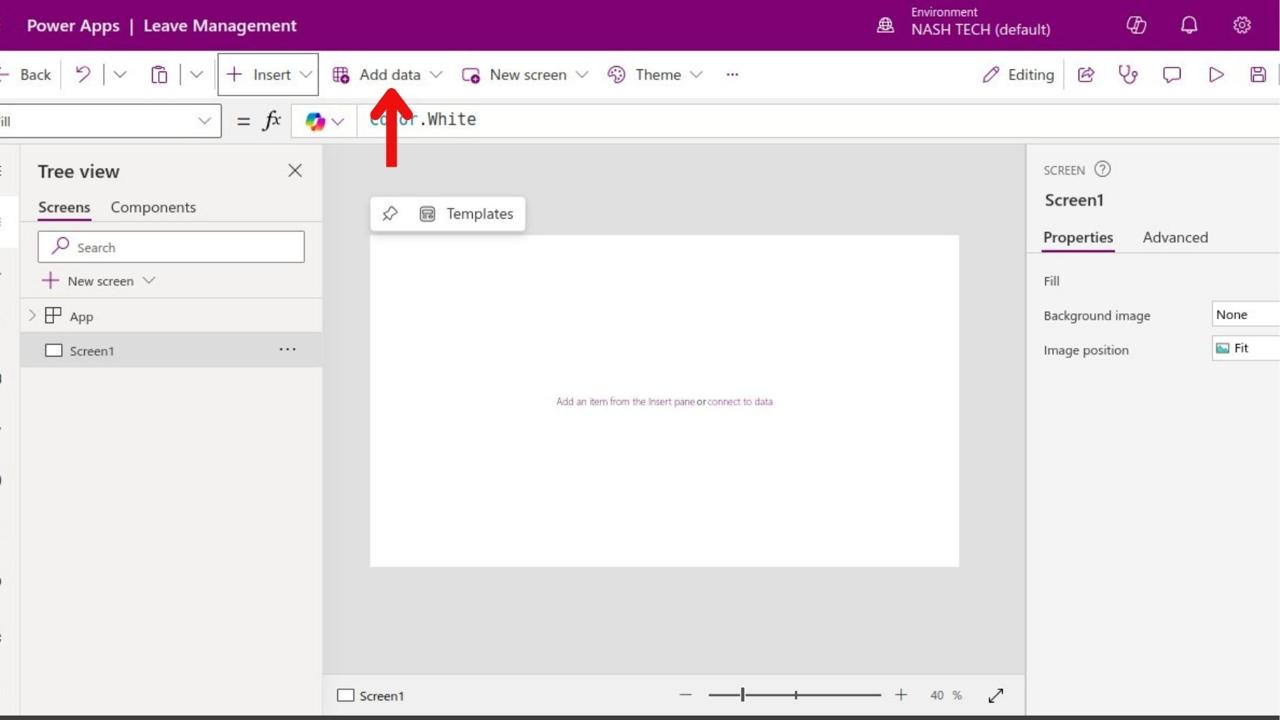
- Add Data: Click the “Data” tab, then “Add data.”
- Select Source: Choose your data source (e.g., Excel, SharePoint). Follow the prompts to connect.
Step 4: Design the User Interface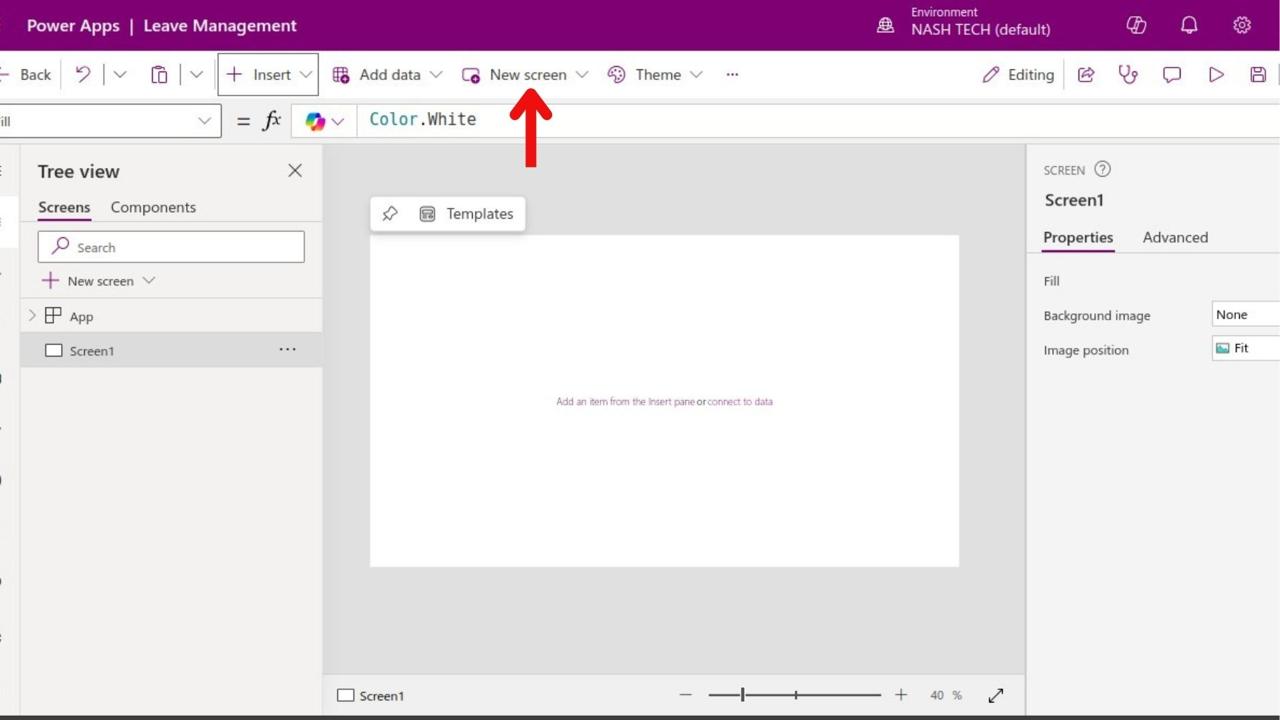
- Add Screens: Click “New Screen” to add more screens.
- Insert Controls: Drag and drop controls (e.g., labels, text boxes, buttons) from the “Insert” tab.
- Customize: Modify properties like text, color, and size in the properties pane.
Step 5: Add Functionality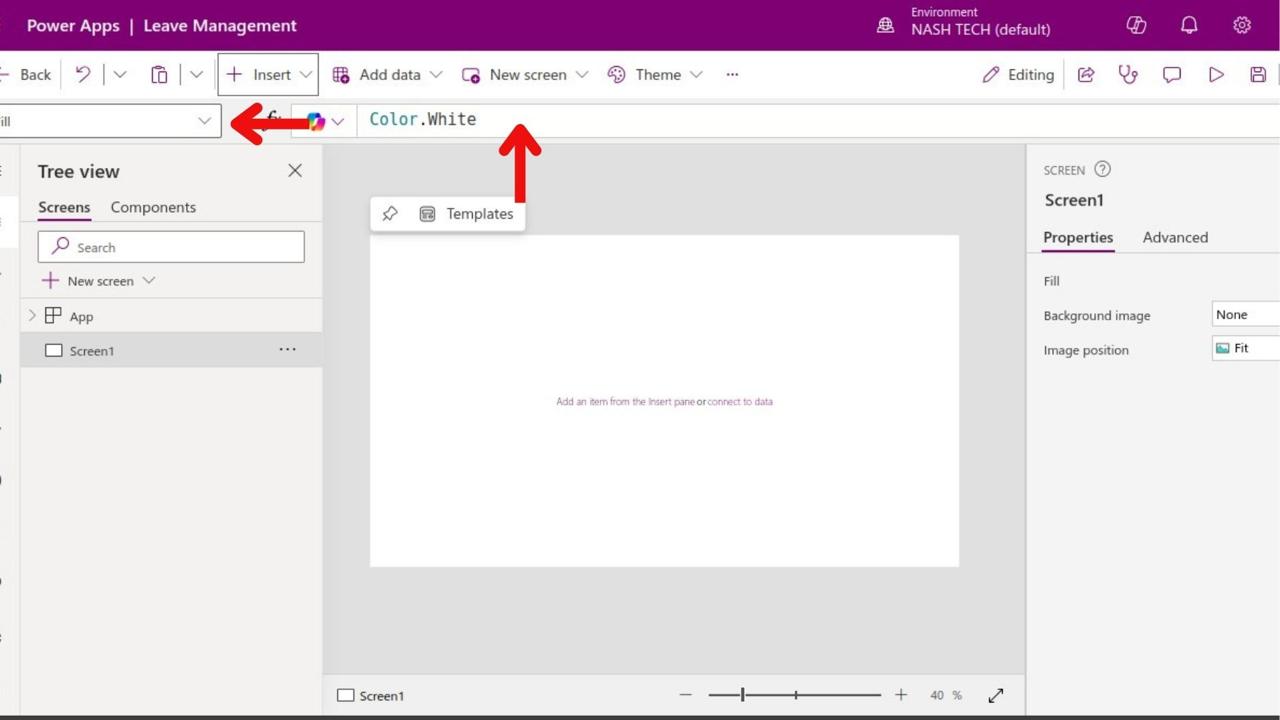
- Set Navigation: Use the “OnSelect” property of buttons for navigation, e.g., Navigate(Screen2, ScreenTransition.Fade).
- Bind Data: Set a gallery’s “Items” property to your data source to display data.
- Add Logic: Use formulas for actions, e.g., If statements for validation.
Step 6: Test Your App
- Preview: Click the play button to test your app.
- Debug: Fix any issues found during testing.
Step 7: Save and Share Your App
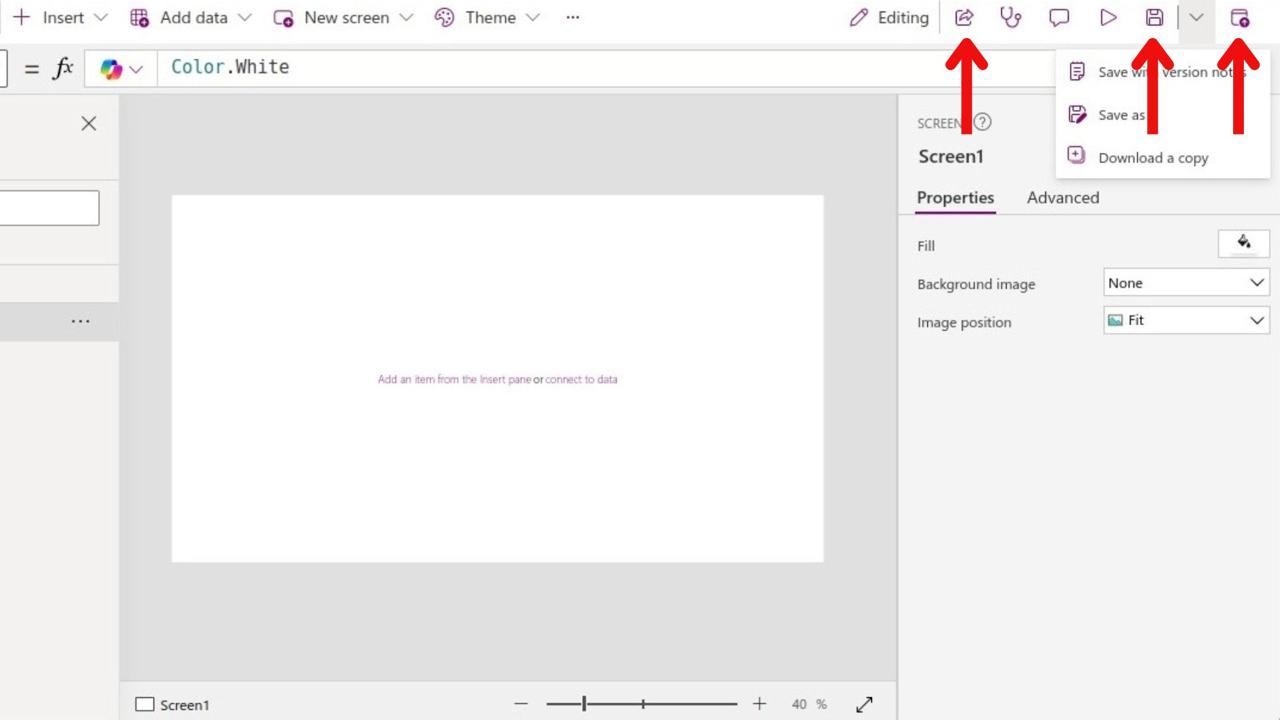
-
Save: Click the file icon and select “Save” to save your app to the cloud.
- Publish: Click “Publish” to make the app available to others.
- If You mistakenly add something inappropriate or irrelevant as per the business so you can opt the older version by just seeing the ‘see all versions tab’ and opt the previous stable version, accordingly, click the three dots and restore and just make sure that our app is closed otherwise not able to restore it.
- Share: Go to the app’s details page, click “Share,” and enter email addresses of users to share with.
Step 8: Deploy and Use Your App
- Access: Users can access the app via the Power Apps mobile app or web portal.
- Gather Feedback: Collect user feedback for improvements.
Some Real-World Application for Power Apps
Power Apps finds applications across various industries and organizational functions. Here are some real-world examples:
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Sales Pipeline Management: Create apps to track leads, opportunities, and customer interactions, streamlining the sales process.
- Customer Support: Build apps for managing customer inquiries, support tickets, and resolutions, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
2. Field Service Management:
- Work Order Tracking: Develop apps for field technicians to receive, update, and complete work orders, enhancing efficiency and communication.
- Asset Management: Create apps for tracking equipment, maintenance schedules, and service histories, ensuring optimal asset performance.
3. Inventory Management:
- Stock Tracking: Build apps to manage inventory levels, track stock movements, and automate reordering processes, reducing stockouts and overstocking.
- Warehouse Operations: Develop apps for barcode scanning, picking, packing, and shipping, streamlining warehouse operations and improving accuracy.
4. Healthcare:
- Patient Management: Create apps for managing patient information, appointments, and medical records, improving patient care coordination and administrative efficiency.
- Telemedicine: Develop apps for virtual consultations, appointment scheduling, and prescription management, facilitating remote healthcare delivery.
5. Education:
- Student Information System: Build apps for managing student enrolment, attendance, grades, and assignments, improving administrative efficiency and student outcomes.
- Learning Management System: Develop apps for delivering course materials, assessments, and communication, enhancing remote and blended learning experiences.
Conclusion
Power Apps is a key tool in the Microsoft Power Platform, allowing users of all skill levels to create custom apps that boost business efficiency. Its intuitive environment supports both canvas and model-driven app creation, integrating seamlessly with various data sources and Microsoft services.
This guide has covered everything from getting started and setting up Power Apps to creating your first app and exploring real-world use cases. Power Apps democratizes app development, enabling users to streamline operations and drive innovation.
As you delve deeper into Power Apps, you’ll discover its potential to transform your business processes and support your digital transformation journey with tailored solutions.


