Welcome to another blog of our Amazon Bedrock deep dive series. In our last article From Console to Code: Prompt Engineering with Amazon Bedrock, we came to know how to engineer prompts programmatically with Amazon Bedrock using Amazon SageMaker Unified Studio (JupyterLab) & boto3. In this blog, we’ll walk through the full process of implementing RAG with Amazon Bedrock. We will also highlight some rough edges and see how to make everything work end‑to‑end.
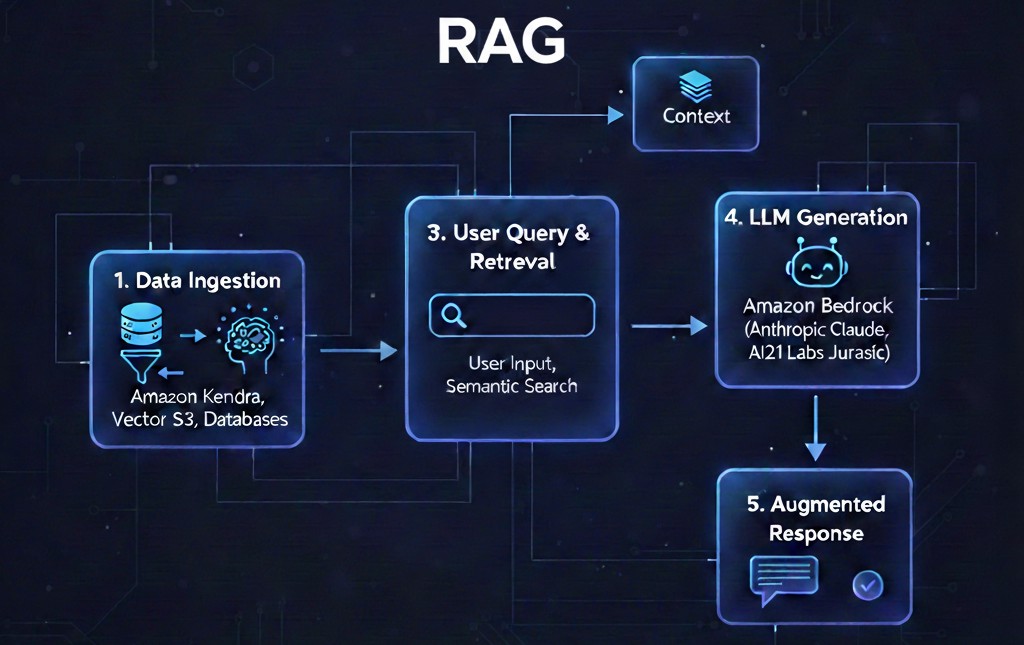
What is RAG?
Retrieval‑Augmented Generation (RAG) is a very valuable pattern in modern AI. It allows applications to pull data from external (or interval) sources and blend it with LLM reasoning to deliver accurate & context‑aware responses. Amazon Bedrock provides a very unique approach to implementing RAG(s), i.e., via Knowledge Bases. Although, this approach introduces a little bit of extra complexity to the process, but it has its own advantages.
Part 1: Create a Knowledge Base
1. Prepare an S3 Bucket
Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases require a location for source documents. If you don’t already have a S3 bucket, please create one:
- Open the S3 console
- Click Create bucket
- Give it a unique name

2. Configure the Knowledge Base Source
Navigate to Amazon Bedrock and following the below instructions:
- Select Knowledge Bases from left panel
- Click Create Knowledge Base with Vector Store
- Choose S3 as the data source (you can also use a web crawler)

- Select your S3 bucket
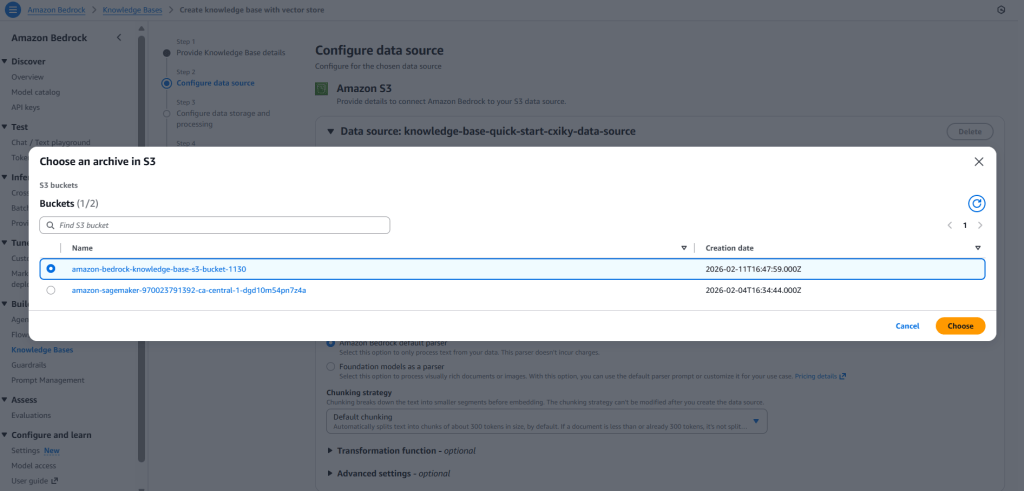
- Keep default chunking for now. It determines how documents are split into chunks for embedding into a vector database.
- Click Next
Part 2: Set Up Vector Store & Embeddings
This is the most crucial and complicated step of implementing a RAG in Amazon Bedrock because this step is where things start getting complex.
1. Embedding Model Selection
Although there are many models available in Amazon Bedrock, depending on your selected region. But for simplicity we will select Titan Embeddings G2 – Text model from Amazon.
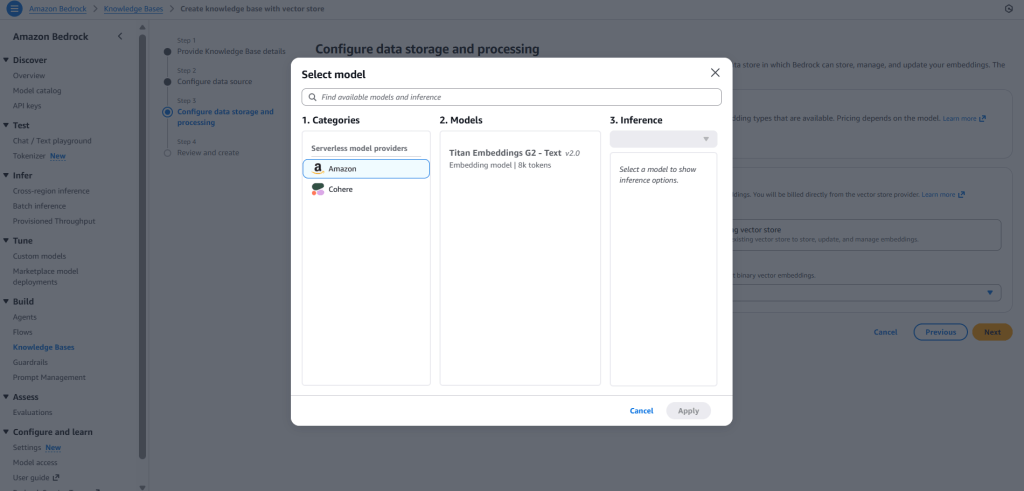
2. Vector Database Options
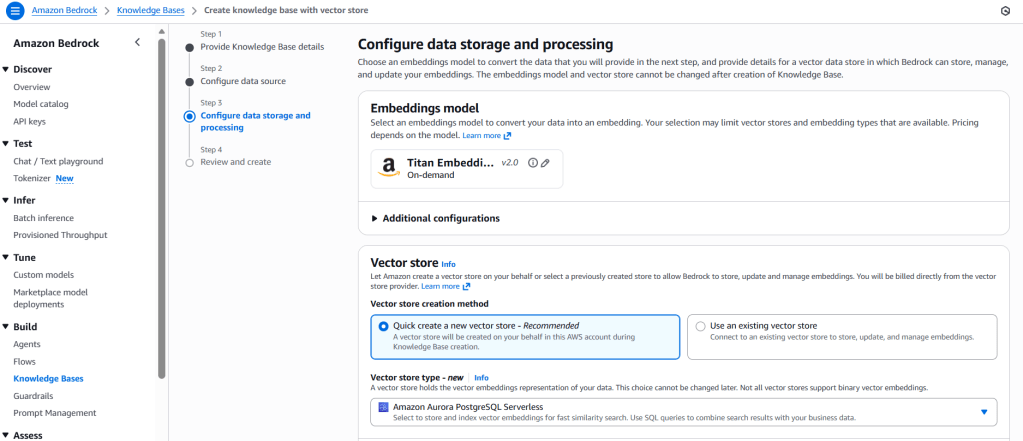
There are multiple options available for vector database from which we can choose. They are:
- Amazon OpenSearch Serverless
- Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL Serverless
- Amazon S3 Vectors (recent addition)
However, for now, we will select Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL Serverless, since it integrates directly and auto‑provisions during setup.
Part 3: Upload Knowledge (Source) Documents
Here, we will use sample Amazon shareholder letters (in PDF format). However, if required, we can use any document(s). A point to remember here is, PDF document(s) require an extra step of extraction before indexing. However, Amazon Bedrock handles the extraction step automatically, so, we don’t need to take any action in that regard.
- Upload the documents to the root folder of the S3 bucket created in part 2

- Return back to Amazon Bedrock
- Navigate to the Knowledge Base created in Part 1
- Select the S3 bucket under the Data Sources
- At last, click on “Sync” to trigger the ingestion pipeline
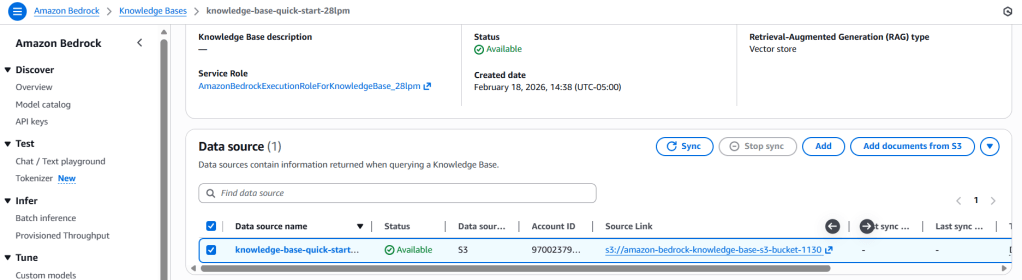
Once sync is complete, the vector store will contain the embedded chunks of the source documents.
Part 4: Retrieving Data (RAG) From Your Knowledge Base
With ingestion completed, we can test retrieval inside the Amazon Bedrock console:
- Navigate to the Knowledge Bases
- Click Retrieval and response generation: data sources and model
- Select an LLM (like Nova 2 Lite, Mistral AI, Anthropic, etc.)
- Ask a question based on the documents
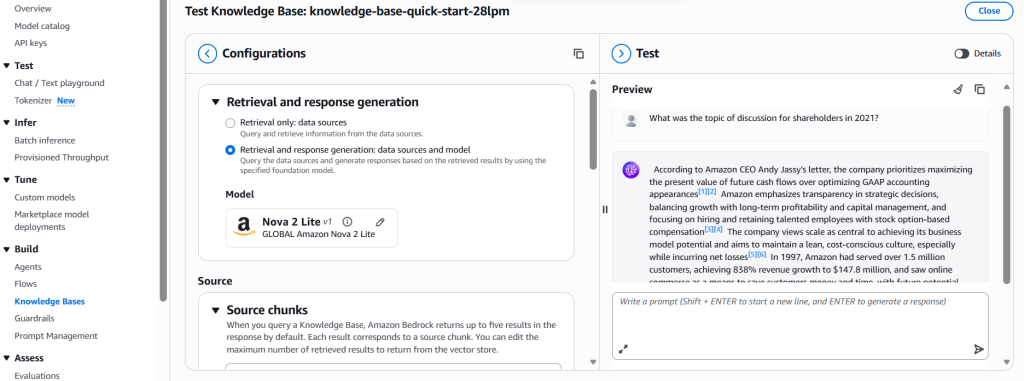
We’ll see the model respond using chunks from the indexed PDF files. This confirms the RAG pipeline is working as expected.
In Summary
Now we have gone through the full implementation journey, i.e., setting up the S3 bucket & Knowledge Base, syncing documents, and testing Knowledge Base. Setting up a RAG workflow in Amazon Bedrock is doable, but it owes some friction in doing so. For instance, we have to navigate to different Amazon services (like S3, Vector DBs, Aurora PostgreSQL, etc.) before we can ask our first question from the RAG. However, once configured a RAG in Amazon Bedrock offers:
- A fully managed ingestion pipeline
- Automatic document chunking & embedding
- Production‑grade vector search through Aurora PostgreSQL
- And much more…
All this makes Amazon Bedrock a capable platform for building RAG‑powered applications.